Characteristics and prognostic factors of synchronous multiple primary esophageal carcinoma: A report of 52 cases
- PMID: 26766968
- PMCID: PMC4704272
- DOI: 10.1111/1759-7714.12047
Characteristics and prognostic factors of synchronous multiple primary esophageal carcinoma: A report of 52 cases
Abstract
Background: To retrospectively analyze the clinical characteristics and prognostic factors of 52 cases of synchronous multiple primary esophageal carcinoma (SMPEC), in order to provide a reference for treatment strategy.
Methods: Clinical and survival data of 52 patients with SMPEC were analyzed retrospectively. The rates of overall survival (OS), depending on the different factors, were calculated using Kaplan-Meier analysis. A log-rank test was used for univariate survival analysis and Cox's proportional hazards regression model was used for multivariate survival analysis.
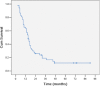
Results: Clinical and survival data of 52 patients with SMPEC, hospitalized from 1 January 2003 to 31 October 2011, were analyzed. Twelve patients underwent surgical resection, five received adjuvant radiotherapy and one received adjuvant radiochemotherapy. Thirty-seven of the 40 non-operative patients received external beam radiation therapy and 20 of them received platinum-based chemotherapy. Another three non-operative patients were given platinum-based chemotherapy alone. The one, three, and five-year OS and the median survival time (MST) were 65.4%, 17.3%, 7.7%, respectively, and 15.0 months for the whole cohort. Tumor length and M stage were independent prognostic factors for the whole cohort by multivariate survival analysis (P = 0.010 and 0.047, respectively). For the radiotherapy subgroup, multivariate analysis of prognostic factors identified that shorter tumor length, M0 stage, and chemotherapy were the predominant independent predictors of long-term survival (P = 0.039, 0.022 and 0.010, respectively).
Conclusions: SMPEC is a relatively rare and aggressive tumor. Combined radiotherapy with chemotherapy seemed to bring a survival benefit and may be a better management choice for unresectable and non-operative SMPEC.
Keywords: Esophageal neoplasm; multiple primary carcinoma; prognosis.
Figures
References
-
- Warren S, Gates O. Multiple primary malignant tumors: a survey of the literature and a statistical study. Am J Cancer. 1932;16:1358–1414.
-
- Xiao ZF, Yang ZY, Wang M, et al. Radiotherapy of multi-focal esophageal carcinoma. Chin J Radiat Oncol. 1989;4:222–224. (In Chinese.)
-
- Morita M, Kuwano H, Nakashima T, et al. Family aggregation of carcinoma of the hypopharynx and cervical esophagus: special reference to multiplicity of cancer in upper aerodigestive tract. Int J Cancer. 1998;76:468–471. - PubMed
-
- Shibuya H, Wakita T, Nakagawa T, Fukuda H, Yasumoto M. The relation between an esophageal cancer and associated cancers in adjacent organs. Cancer. 1995;76:101–105. - PubMed
-
- Pesko P, Rakic S, Milicevic M, Bulajic P, Gerzic Z. Prevalence and clinicopathologic features of multiple squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Cancer. 1994;73:2687–2690. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources