Pemetrexed plus carboplatin as adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with curative resected non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 26766972
- PMCID: PMC4704276
- DOI: 10.1111/1759-7714.12058
Pemetrexed plus carboplatin as adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with curative resected non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: Cisplatin-based adjuvant chemotherapy provided a significant advantage in the overall survival (OS) of patients with stage II and III non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, the compliance and toxicity in cisplatin-based treatment were not always satisfactory. Pemetrexed plus carboplatin (PC) had better chemotherapy compliance and efficiency in advanced non-squamous NSCLC patients. The aim of our study was to investigate the feasibility and efficacy of PC as adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with completely resected non-squamous NSCLC.
Methods: Eighty-two eligible non-squamous NSCLC patients operated on with pathological stage II or IIIA were enrolled in this trial. Adjuvant chemotherapy was initiated between one and four weeks after surgery, and consisted of four cycles of pemetrexed (500 mg/m2) plus carboplatin (AUC = 5) every three weeks. The primary endpoint was the compliance of the regimen and the second endpoint was disease-free survival (DFS).
Results: Patient demographics were median age 58 years (range 32 to 78) and gender ratio 68.3% male/31.7% female. Forty-eight (58.5%) of the patients were at stage II, and the other thirty-four (41.5%) patients were at stage IIIA. Seventy patients (85.4%) received four cycles of therapy over a 12-week period. Reasons for discontinuing therapy included: patient's refusal (n = 10); severe adverse events (n = 1); and surgical complications (n = 1). The primary grade 3 to 4 adverse reaction was hematologic toxicity: neutropenia (13.4%); leucopenia (7.3%); anemia (3.7%); and thrombocytopenia (2.4%). Non-hematological adverse events were mild. No treatment related deaths were observed. Median DFS for stage II and IIIA patients were 38.0 months (95% confidence interval (CI): 28.1 to 47.9 months) and 21.0 months (95%CI: 13.7 to 28.3 months), respectively.
Conclusion: Adjuvant PC chemotherapy was an acceptable regimen in resected non-squamous NSCLC patients.
Keywords: Adjuvant chemotherapy; carboplatin; non-small cell lung cancer; pemetrexed.
Figures
References
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. - PubMed
-
- Winton T, Livingston R, Johnson D, et al. Vinorelbine plus cisplatin vs. observation in resected non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:2589–2597. - PubMed
-
- Ravdin PM, Davis G. Prognosis of patients with resected non-small cell lung cancer: impact of clinical and pathologic variables. Lung Cancer. 2006;52:207–212. - PubMed
-
- Pignon JP, Tribodet H, Scagliotti GV, et al. Lung adjuvant cisplatin evaluation: a pooled analysis by the LACE Collaborative Group. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:3552–3559. - PubMed
-
- Waller D, Peake MD, Stephens RJ, et al. Chemotherapy for patients with non-small cell lung cancer: the surgical setting of the Big Lung Trial. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2004;26:173–182. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

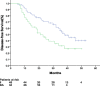
 ,…
,…  , stage IIIA;
, stage IIIA;  , stage II-censored;
, stage II-censored;  …
… 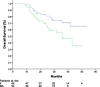
 ,…
,…  , stage IIIA;
, stage IIIA;  , stage II-censored;
, stage II-censored;  …
… 