Angiotensin III increases monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression in cultured human proximal tubular epithelial cells
- PMID: 26767865
- PMCID: PMC4712415
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2016.31.1.116
Angiotensin III increases monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression in cultured human proximal tubular epithelial cells
Abstract
Background/aims: We investigated whether angiotensin III (Ang III) is involved in monocyte recruitment through regulation of the chemokine monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) in cultured human proximal tubular epithelial cells (HK-2 cells).
Methods: We measured MCP-1 levels in HK-2 cells that had been treated with various concentrations of Ang III and Ang II type-1 (AT1) receptor antagonists at various time points. The phosphorylation states of p38, c-Jun N-terminal kinases (JNK), and extracellular-signal-regulated kinases were measured in Ang III-treated cells to explore the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway. MCP-1 levels in HK-2 cell-conditioned media were measured after pre-treatment with the transcription factor inhibitors curcumin or pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate.
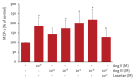
Results: Ang III increased MCP-1 protein production in dose- and time-dependent manners in HK-2 cells, which was inhibited by the AT1 receptor blocker losartan. p38 MAPK activity increased significantly in HK-2 cells exposed to Ang III for 30 minutes, and was sustained at higher levels after 60 minutes (p < 0.05). Total phosphorylated JNK protein levels tended to increase 20 minutes after stimulation with Ang III. Pre-treatment with a p38 inhibitor, a JNK inhibitor, or curcumin significantly inhibited Ang III-induced MCP-1 production.
Conclusions: Ang III increases MCP-1 synthesis via stimulation of intracellular p38 and JNK MAPK signaling activity and subsequent activated protein-1 transcriptional activity in HK-2 cells.
Keywords: Angiotensin III; Chemokine CCL2; Kidney tubules; Mitogen-activated protein kinases; Transcription factors.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures





References
-
- Igic R. A short history of the renin-angiotensin system. Acta Med Salin. 2009;38:8–12.
-
- Capettini LS, Montecucco F, Mach F, Stergiopulos N, Santos RA, da Silva RF. Role of renin-angiotensin system in inflammation, immunity and aging. Curr Pharm Des. 2012;18:963–970. - PubMed
-
- Unger T. The role of the renin-angiotensin system in the development of cardiovascular disease. Am J Cardiol. 2002;89:3A–9A. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
