Improved survival of porcine acute liver failure by a bioartificial liver device implanted with induced human functional hepatocytes
- PMID: 26768767
- PMCID: PMC4746613
- DOI: 10.1038/cr.2016.6
Improved survival of porcine acute liver failure by a bioartificial liver device implanted with induced human functional hepatocytes
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Improved survival of porcine acute liver failure by a bioartificial liver device implanted with induced human functional hepatocytes.Cell Res. 2025 Jun;35(6):469-470. doi: 10.1038/s41422-025-01108-5. Cell Res. 2025. PMID: 40148490 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
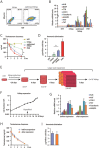
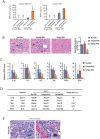
Acute liver failure (ALF) is a life-threatening illness. The extracorporeal cell-based bioartificial liver (BAL) system could bridge liver transplantation and facilitate liver regeneration for ALF patients by providing metabolic detoxification and synthetic functions. Previous BAL systems, based on hepatoma cells and non-human hepatocytes, achieved limited clinical advances, largely due to poor hepatic functions, cumbersome preparation or safety concerns of these cells. We previously generated human functional hepatocytes by lineage conversion (hiHeps). Here, by improving functional maturity of hiHeps and producing hiHeps at clinical scales (3 billion cells), we developed a hiHep-based BAL system (hiHep-BAL). In a porcine ALF model, hiHep-BAL treatment restored liver functions, corrected blood levels of ammonia and bilirubin, and prolonged survival. Importantly, human albumin and α-1-antitrypsin were detectable in hiHep-BAL-treated ALF pigs. Moreover, hiHep-BAL treatment led to attenuated liver damage, resolved inflammation and enhanced liver regeneration. Our findings indicate a promising clinical application of the hiHep-BAL system.
Figures

References
-
- 1Bernal W, Wendon J. Acute liver failure. N Engl J Med 2013; 369:2525–2534. - PubMed
-
- 2Struecker B, Raschzok N, Sauer IM. Liver support strategies: cutting-edge technologies. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2014; 11:166–176. - PubMed
-
- 3Sussman NL, Kelly JH. Artificial liver. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2014; 12:1439–1442. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

