New Wistar Kyoto and spontaneously hypertensive rat transgenic models with ubiquitous expression of green fluorescent protein
- PMID: 26769799
- PMCID: PMC4852507
- DOI: 10.1242/dmm.024208
New Wistar Kyoto and spontaneously hypertensive rat transgenic models with ubiquitous expression of green fluorescent protein
Abstract
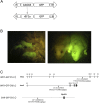
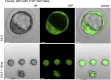
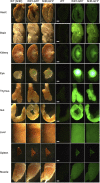
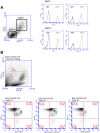
The Wistar Kyoto (WKY) rat and the spontaneously hypertensive (SHR) rat inbred strains are well-established models for human crescentic glomerulonephritis (CRGN) and metabolic syndrome, respectively. Novel transgenic (Tg) strains add research opportunities and increase scientific value to well-established rat models. We have created two novel Tg strains using Sleeping Beauty transposon germline transgenesis, ubiquitously expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP) under the rat elongation factor 1 alpha (EF1a) promoter on the WKY and SHR genetic backgrounds. The Sleeping Beauty system functioned with high transgenesis efficiency; 75% of new rats born after embryo microinjections were transgene positive. By ligation-mediated PCR, we located the genome integration sites, confirming no exonic disruption and defining a single or low copy number of the transgenes in the new WKY-GFP and SHR-GFP Tg lines. We report GFP-bright expression in embryos, tissues and organs in both lines and show preliminaryin vitroandin vivoimaging data that demonstrate the utility of the new GFP-expressing lines for adoptive transfer, transplantation and fate mapping studies of CRGN, metabolic syndrome and other traits for which these strains have been extensively studied over the past four decades.
Keywords: GFP; Rat; SHR; Transgenics; WKY.
© 2016. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Aitman T. J., Gotoda T., Evans A. L., Imrie H., Heath K. E., Trembling P. M., Truman H., Wallace C. A., Rahman A., Doré C. et al. (1997). Quantitative trait loci for cellular defects in glucose and fatty acid metabolism in hypertensive rats. Nat. Genet. 16, 197-201. 10.1038/ng0697-197 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aitman T. J., Glazier A. M., Wallace C. A., Cooper L. D., Norsworthy P. J., Wahid F. N., Al-Majali K. M., Trembling P. M., Mann C. J., Shoulders C. C. et al. (1999). Identification of Cd36 (Fat) as an insulin-resistance gene causing defective fatty acid and glucose metabolism in hypertensive rats. Nat. Genet. 21, 76-83. 10.1038/5013 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

