Phosphorylation of TAR DNA-binding Protein of 43 kDa (TDP-43) by Truncated Casein Kinase 1δ Triggers Mislocalization and Accumulation of TDP-43
- PMID: 26769969
- PMCID: PMC4786690
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.695379
Phosphorylation of TAR DNA-binding Protein of 43 kDa (TDP-43) by Truncated Casein Kinase 1δ Triggers Mislocalization and Accumulation of TDP-43
Abstract
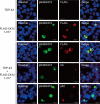
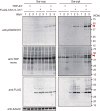
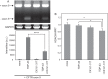
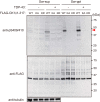
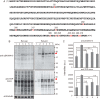
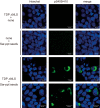
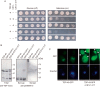
Intracellular aggregates of phosphorylated TDP-43 are a major component of ubiquitin-positive inclusions in the brains of patients with frontotemporal lobar degeneration and ALS and are considered a pathological hallmark. Here, to gain insight into the mechanism of intracellular TDP-43 accumulation, we examined the relationship between phosphorylation and aggregation of TDP-43. We found that expression of a hyperactive form of casein kinase 1 δ (CK1δ1-317, a C-terminally truncated form) promotes mislocalization and cytoplasmic accumulation of phosphorylated TDP-43 (ubiquitin- and p62-positive) in cultured neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Insoluble phosphorylated TDP-43 prepared from cells co-expressing TDP-43 and CK1δ1-317 functioned as seeds for TDP-43 aggregation in cultured cells, indicating that CK1δ1-317-induced aggregated TDP-43 has prion-like properties. A striking toxicity and alterations of TDP-43 were also observed in yeast expressing TDP-43 and CK1δ1-317. Therefore, abnormal activation of CK1δ causes phosphorylation of TDP-43, leading to the formation of cytoplasmic TDP-43 aggregates, which, in turn, may trigger neurodegeneration.
Keywords: ALS (Lou Gehrig disease); TAR DNA-binding protein of 43 kDa (TDP-43); casein kinase 1δ; frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD); phosphorylation; protein aggregation; protein kinase.
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Casein Kinase 1δ Phosphorylates TDP-43 and Suppresses Its Function in Tau mRNA Processing.J Alzheimers Dis. 2023;91(4):1527-1539. doi: 10.3233/JAD-220985. J Alzheimers Dis. 2023. PMID: 36641675
-
Inositol Hexakisphosphate Kinase 2 Promotes Cell Death in Cells with Cytoplasmic TDP-43 Aggregation.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Oct;53(8):5377-83. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9470-1. Epub 2015 Oct 6. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26440668
-
CK1δ/ε kinases regulate TDP-43 phosphorylation and are therapeutic targets for ALS-related TDP-43 hyperphosphorylation.Neurobiol Dis. 2024 Jun 15;196:106516. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2024.106516. Epub 2024 Apr 25. Neurobiol Dis. 2024. PMID: 38677657
-
[Neurodegenerative disorders and TDP-43].Brain Nerve. 2009 Feb;61(2):161-6. Brain Nerve. 2009. PMID: 19235466 Review. Japanese.
-
[The molecular mechanisms of intracellular TDP-43 aggregates].Brain Nerve. 2009 Nov;61(11):1292-300. Brain Nerve. 2009. PMID: 19938686 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Dysregulation of RNA-Binding Proteins in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis.Front Mol Neurosci. 2020 May 29;13:78. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2020.00078. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32547363 Free PMC article.
-
TDP-43/FUS in motor neuron disease: Complexity and challenges.Prog Neurobiol. 2016 Oct-Nov;145-146:78-97. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2016.09.004. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Prog Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 27693252 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Mechanisms Underlying TDP-43 Pathology in Cellular and Animal Models of ALS and FTLD.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 29;22(9):4705. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094705. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33946763 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elevation of casein kinase 1ε associated with TDP-43 and tau pathologies in Alzheimer's disease.Brain Pathol. 2020 Mar;30(2):283-297. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12775. Epub 2019 Aug 22. Brain Pathol. 2020. PMID: 31376192 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms underlying TDP-43 pathology and neurodegeneration: An updated Mini-Review.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 Mar 9;15:1142617. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1142617. eCollection 2023. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36967829 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arai T., Hasegawa M., Akiyama H., Ikeda K., Nonaka T., Mori H., Mann D., Tsuchiya K., Yoshida M., Hashizume Y., and Oda T. (2006) TDP-43 is a component of ubiquitin-positive tau-negative inclusions in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 351, 602–611 - PubMed
-
- Neumann M., Sampathu D. M., Kwong L. K., Truax A. C., Micsenyi M. C., Chou T. T., Bruce J., Schuck T., Grossman M., Clark C. M., McCluskey L. F., Miller B. L., Masliah E., Mackenzie I. R., Feldman H., Feiden W., Kretzschmar H. A., Trojanowski J. Q., and Lee V. M. (2006) Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 314, 130–133 - PubMed
-
- Ayala Y. M., Zago P., D'Ambrogio A., Xu Y. F., Petrucelli L., Buratti E., and Baralle F. E. (2008) Structural determinants of the cellular localization and shuttling of TDP-43. J. Cell Sci. 121, 3778–3785 - PubMed
-
- Buratti E., and Baralle F. E. (2008) Multiple roles of TDP-43 in gene expression, splicing regulation, and human disease. Front. Biosci. 13, 867–878 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

