Phosphorylation of TAR DNA-binding Protein of 43 kDa (TDP-43) by Truncated Casein Kinase 1δ Triggers Mislocalization and Accumulation of TDP-43
- PMID: 26769969
- PMCID: PMC4786690
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.695379
Phosphorylation of TAR DNA-binding Protein of 43 kDa (TDP-43) by Truncated Casein Kinase 1δ Triggers Mislocalization and Accumulation of TDP-43
Abstract
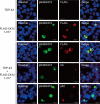
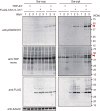
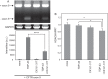
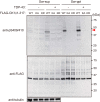
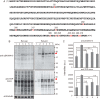
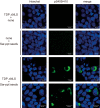
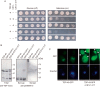
Intracellular aggregates of phosphorylated TDP-43 are a major component of ubiquitin-positive inclusions in the brains of patients with frontotemporal lobar degeneration and ALS and are considered a pathological hallmark. Here, to gain insight into the mechanism of intracellular TDP-43 accumulation, we examined the relationship between phosphorylation and aggregation of TDP-43. We found that expression of a hyperactive form of casein kinase 1 δ (CK1δ1-317, a C-terminally truncated form) promotes mislocalization and cytoplasmic accumulation of phosphorylated TDP-43 (ubiquitin- and p62-positive) in cultured neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Insoluble phosphorylated TDP-43 prepared from cells co-expressing TDP-43 and CK1δ1-317 functioned as seeds for TDP-43 aggregation in cultured cells, indicating that CK1δ1-317-induced aggregated TDP-43 has prion-like properties. A striking toxicity and alterations of TDP-43 were also observed in yeast expressing TDP-43 and CK1δ1-317. Therefore, abnormal activation of CK1δ causes phosphorylation of TDP-43, leading to the formation of cytoplasmic TDP-43 aggregates, which, in turn, may trigger neurodegeneration.
Keywords: ALS (Lou Gehrig disease); TAR DNA-binding protein of 43 kDa (TDP-43); casein kinase 1δ; frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD); phosphorylation; protein aggregation; protein kinase.
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Arai T., Hasegawa M., Akiyama H., Ikeda K., Nonaka T., Mori H., Mann D., Tsuchiya K., Yoshida M., Hashizume Y., and Oda T. (2006) TDP-43 is a component of ubiquitin-positive tau-negative inclusions in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 351, 602–611 - PubMed
-
- Neumann M., Sampathu D. M., Kwong L. K., Truax A. C., Micsenyi M. C., Chou T. T., Bruce J., Schuck T., Grossman M., Clark C. M., McCluskey L. F., Miller B. L., Masliah E., Mackenzie I. R., Feldman H., Feiden W., Kretzschmar H. A., Trojanowski J. Q., and Lee V. M. (2006) Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 314, 130–133 - PubMed
-
- Ayala Y. M., Zago P., D'Ambrogio A., Xu Y. F., Petrucelli L., Buratti E., and Baralle F. E. (2008) Structural determinants of the cellular localization and shuttling of TDP-43. J. Cell Sci. 121, 3778–3785 - PubMed
-
- Buratti E., and Baralle F. E. (2008) Multiple roles of TDP-43 in gene expression, splicing regulation, and human disease. Front. Biosci. 13, 867–878 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

