The Korean Cough Guideline: Recommendation and Summary Statement
- PMID: 26770230
- PMCID: PMC4701789
- DOI: 10.4046/trd.2016.79.1.14
The Korean Cough Guideline: Recommendation and Summary Statement
Abstract
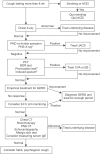
Cough is one of the most common symptom of many respiratory diseases. The Korean Academy of Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases organized cough guideline committee and cough guideline was developed by this committee. The purpose of this guideline is to help clinicians to diagnose correctly and treat efficiently patients with cough. In this article, we have stated recommendation and summary of Korean cough guideline. We also provided algorithm for acute, subacute, and chronic cough. For chronic cough, upper airway cough syndrome (UACS), cough variant asthma (CVA), and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) should be considered. If UACS is suspicious, first generation anti-histamine and nasal decongestant can be used empirically. In CVA, inhaled corticosteroid is recommended in order to improve cough. In GERD, proton pump inhibitor is recommended in order to improve cough. Chronic bronchitis, bronchiectasis, bronchiolitis, lung cancer, aspiration, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor, habit, psychogenic cough, interstitial lung disease, environmental and occupational factor, tuberculosis, obstructive sleep apnea, peritoneal dialysis, and idiopathic cough can be also considered as cause of chronic cough. Level of evidence for treatment is mostly low. Thus, in this guideline, many recommendations are based on expert opinion. Further study regarding treatment for cough is mandatory.
Keywords: Cough; Guideline; Korean.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Madison JM, Irwin RS. Pharmacotherapy of chronic cough in adults. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2003;4:1039–1048. - PubMed
-
- Gaffey MJ, Kaiser DL, Hayden FG. Ineffectiveness of oral terfenadine in natural colds: evidence against histamine as a mediator of common cold symptoms. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1988;7:223–228. - PubMed
-
- Berkowitz RB, Connell JT, Dietz AJ, Greenstein SM, Tinkelman DG. The effectiveness of the nonsedating antihistamine loratadine plus pseudoephedrine in the symptomatic management of the common cold. Ann Allergy. 1989;63:336–339. - PubMed
-
- Gwaltney JM, Jr, Phillips CD, Miller RD, Riker DK. Computed tomographic study of the common cold. N Engl J Med. 1994;330:25–30. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

