Prognostic Impact and Clinicopathological Correlation of CD133 and ALDH1 Expression in Invasive Breast Cancer
- PMID: 26770241
- PMCID: PMC4705086
- DOI: 10.4048/jbc.2015.18.4.347
Prognostic Impact and Clinicopathological Correlation of CD133 and ALDH1 Expression in Invasive Breast Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: CD133 and aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 (ALDH1) expression are reliable poor-prognosis markers associated with the presence of adverse biomarkers and subtypes of breast cancer. The aim of our study was to investigate and compare the clinical impact of CD133 and ALDH1 expression in invasive breast cancer.
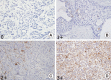
Methods: A total of 291 consecutive patients with invasive breast cancer who underwent breast cancer operations from 2005 to 2010 at a single institution were included in this retrospective review. CD133 and ALDH1 expression were determined by immunohistochemistry.
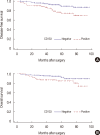
Results: CD133 and ALDH1 expression were positive in 24.7% and 22.0% of the patients, respectively, and were associated with tumor size, cancer stage, estrogen receptor negativity, nonluminal subtype, triple-negative breast cancer, and recurrence. CD133 expression was significantly associated with lymph node metastasis, progesterone receptor negativity, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 positivity, chemotherapy, and poor disease-free (p=0.002) and overall survival (p=0.014), but ALDH1 expression was not. Cancer stage (p<0.001) was an independent prognostic factor for disease-free survival in multivariate analysis. Cancer stage (p<0.001) and receipt of radiotherapy (p=0.045) were independent prognostic factors for overall survival in multivariate analysis.
Conclusion: CD133 or the combination of CD133 and ALDH1 expression were more widely associated with the presence of adverse biomarkers and subtypes of breast cancer, compared to ALDH1 expression alone, and these markers may have a potential predictive role and be a helpful tool in the management for patients with invasive breast cancer.
Keywords: Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1; Breast neoplasms; CD133 antigen; Prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Comment in
-
Comments on the "Prognostic Impact and Clinicopathological Correlation of CD133 and ALDH1 Expression in Invasive Breast Cancer" and the "Commentary by Antonio Ieni and Giovanni Tuccari".J Breast Cancer. 2016 Sep;19(3):336-338. doi: 10.4048/jbc.2016.19.3.336. Epub 2016 Sep 23. J Breast Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27721886 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Resetkova E, Reis-Filho JS, Jain RK, Mehta R, Thorat MA, Nakshatri H, et al. Prognostic impact of ALDH1 in breast cancer: a story of stem cells and tumor microenvironment. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010;123:97–108. - PubMed
-
- Tsang JY, Huang YH, Luo MH, Ni YB, Chan SK, Lui PC, et al. Cancer stem cell markers are associated with adverse biomarker profiles and molecular subtypes of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012;136:407–417. - PubMed
-
- Chuthapisith S, Eremin J, El-Sheemey M, Eremin O. Breast cancer chemoresistance: emerging importance of cancer stem cells. Surg Oncol. 2010;19:27–32. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

