Sildenafil dilates ophthalmic artery in type 2 diabetic patients
- PMID: 26770675
- PMCID: PMC4687761
- DOI: 10.1177/2050312113495195
Sildenafil dilates ophthalmic artery in type 2 diabetic patients
Abstract
Background: Conflicting reports exist on the effect of sildenafil on ophthalmic artery blood flow; many visual disturbances due to vascular insult were reported with the use of sildenafil in diabetic patients like nonarteritic ischemic optic neuropathy.
Objectives: The present work aimed to investigate whether sildenafil modulates ophthalmic artery vasoreactivity in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Literature reports on this aspect are lacking.
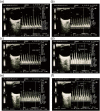
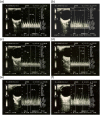
Methods: A total of 35 male subjects were enrolled in this study, 18 with type 2 diabetes mellitus matched with 17 normal individuals. Ophthalmic artery was insonated through a transorbital window using colored Doppler equipment with transcranial Doppler facility. Ophthalmic artery reactivity was assessed using breath holding/hyperventilation test, before and after giving 50 mg oral sildenafil.
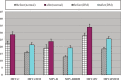
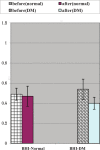
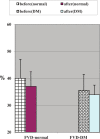
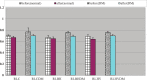
Results: It was found that in both normal subjects and diabetic patients, sildenafil increased baseline control of mean flow velocity of ophthalmic artery significantly (p < 0.05), breath holding caused a decrease of MFVopa (p < 0.05), and subsequent hyperventilation caused increase of MFVopa (p < 0.05). There was no statistically significant change in breath holding index and full range of vasodilatation of ophthalmic artery (p > 0.05) after sildenafil, in normal and diabetic groups. There was a significant increase of resistive index of ophthalmic artery flow in diabetic patients compared with that of normal subject (p < 0.05). Sildenafil decreased resistive index of ophthalmic artery flow significantly only in diabetic patients (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: Sildenafil increased MFVopa, but had no significant effect on vasoreactivity of ophthalmic artery; sildenafil decreased resistive index only in type 2 diabetic patients.
Keywords: Sildenafil; ophthalmic artery; transcranial Doppler; vasoreactivity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Autonomic cerebral vascular response to sildenafil in diabetic patient.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2012 Jan 27;4(1):2. doi: 10.1186/1758-5996-4-2. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2012. PMID: 22284589 Free PMC article.
-
Color Doppler Imaging Analysis of Retrobulbar Blood Flow Velocities in Diabetic Patients Without or With Retinopathy: A Meta-analysis.J Ultrasound Med. 2014 Aug;33(8):1381-9. doi: 10.7863/ultra.33.8.1381. J Ultrasound Med. 2014. PMID: 25063403
-
Effect of hyperbaric oxygen on ophthalmic artery blood velocity in patients with diabetic neuropathy.Jpn J Ophthalmol. 1998 Sep-Oct;42(5):406-10. doi: 10.1016/s0021-5155(98)00029-x. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 1998. PMID: 9822973
-
The effects of sildenafil on ocular blood flow.Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2005 Jun;83(3):355-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0420.2005.00422.x. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2005. PMID: 15948790 Clinical Trial.
-
Ocular arterial flow hemodynamics in patients with diabetes mellitus.J Ultrasound Med. 1998 Nov;17(11):675-81. doi: 10.7863/jum.1998.17.11.675. J Ultrasound Med. 1998. PMID: 9805302
References
-
- Roufail E, Stringer M, Rees S. Nitric oxide synthase immunoreactivity and NADPH diaphorase staining are co-localized in neurons closely associated with the vasculature in rat and human retina. Brain Res 1995; 684: 36–46. - PubMed
-
- Boolell M, Allen MJ, Ballard S, et al. Sildenafil: an orally active type 5 cyclic GMP-specific phosphodiesterase inhibitor for the treatment of penile erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res 1996; 8: 47–52. - PubMed
-
- Yao K, Tschudi M, Flammer J, et al. Endothelium dependent regulation of vascular tone of the porcine ophthalmic artery. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1991; 32: 1791–1798. - PubMed
-
- Sinclair AM, Hughes AD, Sever PS. Effect of nifedipine and glyceryl trinitrate on retinal blood flow in normal subjects. J Hum Hypertens 1993; 7: 399–401. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

