Hsp90 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
- PMID: 26770832
- PMCID: PMC4681826
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/757694
Hsp90 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
Abstract
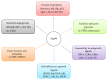
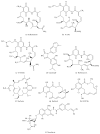
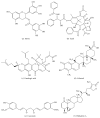
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is a hematological malignancy that arises due to reciprocal translocation of 3' sequences from c-Abelson (ABL) protooncogene of chromosome 9 with 5' sequence of truncated break point cluster region (BCR) on chromosome 22. BCR-ABL is a functional oncoprotein p210 that exhibits constitutively activated tyrosine kinase causing genomic alteration of hematopoietic stem cells. BCR-ABL specific tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) successfully block CML progression. However, drug resistance owing to BCR-ABL mutations and overexpression is still an issue. Heat-shock proteins (Hsps) function as molecular chaperones facilitating proper folding of nascent polypeptides. Their increased expression under stressful conditions protects cells by stabilizing unfolded or misfolded peptides. Hsp90 is the major mammalian protein and is required by BCR-ABL for stabilization and maturation. Hsp90 inhibitors destabilize the binding of BCR-ABL protein thus leading to the formation of heteroprotein complex that is eventually degraded by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Results of many novel Hsp90 inhibitors that have entered into various clinical trials are encouraging. The present review targets the current development in the CML treatment by availing Hsp90 specific inhibitors.
Figures





References
-
- Tefferi A. Classification, diagnosis and management of myeloproliferative disorders in the JAK2V617F era. Hematology. 2006:240–245. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

