Heterotopic Pancreas Presented as Duodenal Tumor with Obstruction
- PMID: 26770904
- PMCID: PMC4712542
- DOI: 10.5223/pghn.2015.18.4.280
Heterotopic Pancreas Presented as Duodenal Tumor with Obstruction
Abstract
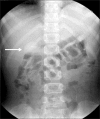
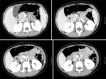
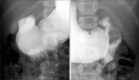
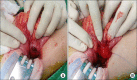
Heterotopic pancreas (HP) is defined as pancreatic tissue lacking anatomic and vascular continuity with the main body of the pancreas. Most are asymptomatic, but can cause ulcer, bleeding, intussusception, and mechanical obstruction. Herein, we presented one case of HP presented as duodenal tumor causing duodenal obstruction. A 7-year-old girl visited the emergency room for abdominal pain with vomiting for 24 hours. Computed tomography and upper gastrointestinal series revealed a polypoid mass with short stalk in the 2nd portion of duodenum. We attempted an endoscopic removal. However, the lumen was nearly obstructed by the mass and the stalk was too broad and hard to excise. The mass was surgically removed via duodenotomy. It was confirmed as a HP with ductal and acini components (type 2 by Heinrich classification). Postoperatively, the patient has been well without any complication and recurrence.
Keywords: Duodenal neoplasms; Duodenal obstruction; Heterotopic pancreas; Pancreas.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Laparoscopic surgery for duodenal perforation due to a diverticulum with heterotopic pancreas: a case report.Surg Case Rep. 2022 Jun 1;8(1):106. doi: 10.1186/s40792-022-01460-3. Surg Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 35648320 Free PMC article.
-
Concurrent Invasive Ductal Carcinoma and Pancreatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia in Duodenal Heterotopic Pancreas: A Case Report.Oman Med J. 2024 Nov 30;39(6):e699. doi: 10.5001/omj.2024.35. eCollection 2024 Nov. Oman Med J. 2024. PMID: 40225110 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical classification of symptomatic heterotopic pancreas of the stomach and duodenum: A case series and systematic literature review.World J Gastroenterol. 2022 Apr 14;28(14):1455-1478. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i14.1455. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35582670 Free PMC article.
-
Duodenal heterotopic pancreas in a child.World J Pediatr. 2009 May;5(2):146-8. doi: 10.1007/s12519-009-0029-y. Epub 2009 Jul 9. World J Pediatr. 2009. PMID: 19718539
-
EUS mini probes in diagnosis of cystic dystrophy of duodenal wall in heterotopic pancreas: a case report.World J Gastroenterol. 2004 Sep 1;10(17):2609-12. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i17.2609. World J Gastroenterol. 2004. PMID: 15300920 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Laparoscopy in the Management of a Diagnostic Dilemma: Jejunal Ectopic Pancreas Developing into Jejunojejunal Intussusception.Case Rep Surg. 2017;2017:8452947. doi: 10.1155/2017/8452947. Epub 2017 Jul 27. Case Rep Surg. 2017. PMID: 28819577 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lai EC, Tompkins RK. Heterotopic pancreas. Review of a 26 year experience. Am J Surg. 1986;151:697–700. - PubMed
-
- Tolentino LF, Lee H, Maung T, Stabile BE, Li K, French SW. Islet cell tumor arising from a heterotopic pancreas in the duodenal wall with ulceration. Exp Mol Pathol. 2004;76:51–56. - PubMed
-
- De Castro Barbosa JJ, Dockerty MB, Waugh JM. Pancreatic heterotopia; review of the literature and report of 41 authenticated surgical cases, of which 25 were clinically significant. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1946;82:527–542. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous