Bilateral Sequential Pneumolabyrinth Resulting from Nose Blowing
- PMID: 26771019
- PMCID: PMC4704557
- DOI: 10.7874/jao.2015.19.3.182
Bilateral Sequential Pneumolabyrinth Resulting from Nose Blowing
Abstract
Pneumolabyrinth describes a condition with entrapped air in the labyrinth and usually occurs in temporal bone fractures that involve the otic capsule. While sporadic cases of bilateral pneumolabyrinth have been reported, cases lacking head trauma are very rare. We report the case of a 43-year-old man who had sudden hearing loss bilaterally after blowing his nose at an interval of 1 year. Although conservative management for the right ear and exploratory tympanotomy with sealing of the possible site of perilymphatic leakage in the left ear were performed, hearing outcome was poor in both ears. To our knowledge, this is the first case of bilateral pneumolabyrinth occurring as a result of nose blowing.
Keywords: Hearing loss; Perilymphatic fistula; Pneumolabyrinth; Valsalva maneuver.
Figures
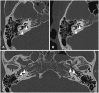
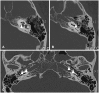
References
-
- Prisman E, Ramsden JD, Blaser S, Papsin B. Traumatic perilymphatic fistula with pneumolabyrinth: diagnosis and management. Laryngoscope. 2011;121:856–859. - PubMed
-
- Woo HJ, Song SY, Kim YD, Bai CH. Pneumolabyrinth without temporal bone fracture: different outcomes for hearing recovery. Laryngoscope. 2008;118:1464–1466. - PubMed
-
- Pullen FW., 2nd Perilymphatic fistula induced by barotrauma. Am J Otol. 1992;13:270–272. - PubMed
-
- Mun SK, Lee KH, Yang HS, Hong YH. Pneumolabyrinth resulting from trauma: report of two cases. Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2008;51:273–277.
-
- Lee EJ, Yang YS, Yoon YJ. Case of bilateral pneumolabyrinth presenting as sudden, bilateral deafness, without temporal bone fracture, after a fall. J Laryngol Otol. 2012;126:717–720. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

