Determining an Optimal Cutoff of Serum β-Human Chorionic Gonadotropin for Assisting the Diagnosis of Intracranial Germinomas
- PMID: 26771195
- PMCID: PMC4714805
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147023
Determining an Optimal Cutoff of Serum β-Human Chorionic Gonadotropin for Assisting the Diagnosis of Intracranial Germinomas
Abstract
Background: Beta (β)-human chorionic gonadotropin (β-HCG) is used to confirm the diagnosis and plan treatment of intracranial germinomas. However, the cutoff values of serum β-HCG in diagnosis of intracranial germinomas reported in the literature are inconsistent. To establish an appropriate cutoff value of serum β-HCG for diagnosis of intracranial germinomas, we retrospectively reviewed the records of intracranial tumor patients who received serum β-HCG and α-fetoprotein (AFP) tests for diagnostic purposes at our hospital from 2005 to 2014.
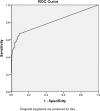
Methods: A total of 93 intracranial germinomas and 289 intracranial non-germ cell tumors were included in this study. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was used to evaluate the sensitivity and specificity of 3 cutoffs (0.1, 0.4, and 0.5 mIU/mL) for diagnosing intracranial germinomas. The serum β-HCG level of intracranial germinoma patients was further analyzed to investigate the effect of metastasis status and tumor location on serum β-HCG level.
Results: The area under the ROC curve was 0.81 (P < .001), suggesting β-HCG is an effective marker. Of the 3 cutoff values, 0.1 mIU/mL possessed a highest sensitivity (66.67%) and good specificity (91%). Although there was no β-HCG level difference between metastatic and non-metastatic intracranial germinoma patients, the diagnostic rate of metastatic neurohypophyseal germinomas was significantly higher than that of its non-metastatic counterpart (P < .05), implying that the location of the germinoma might need to be considered when β-HCG is used as a marker to predict metastasis.
Conclusions: Determining an optimal cutoff of serum β-HCG is helpful for assisting the diagnosis of intracranial germinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Significance of human chorionic gonadotropin as a predictor of resistance to standard chemo-radiotherapy for pure germinoma.Neurosurg Rev. 2018 Apr;41(2):557-565. doi: 10.1007/s10143-017-0891-3. Epub 2017 Aug 18. Neurosurg Rev. 2018. PMID: 28819802
-
[Diagnostic value of serum levels of β-human chorionic gonadotropin (β-hcG) combined with β-hcG in cerebrospinal fluid for determining locations of germinomas in children with precocious puberty].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2010 Oct;48(10):771-4. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 21176488 Chinese.
-
Human chorionic gonadotropin detection in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with a germinoma and its prognostic significance: assessment by using a highly sensitive enzyme immunoassay.J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2016 Nov;18(5):573-577. doi: 10.3171/2016.4.PEDS1658. Epub 2016 Jul 8. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2016. PMID: 27391806
-
Intracranial germ cell tumors.Oncologist. 2000;5(4):312-20. Oncologist. 2000. PMID: 10964999 Review.
-
Intracranial Germinoma Masquerading as Secondary Granulomatous Hypophysitis: A Case Report and Review of Literature.Neuroendocrinology. 2020;110(5):422-429. doi: 10.1159/000501886. Epub 2019 Jul 4. Neuroendocrinology. 2020. PMID: 31269501 Review.
Cited by
-
Pineal/germ cell tumors and pineal parenchymal tumors.Childs Nerv Syst. 2023 Oct;39(10):2649-2665. doi: 10.1007/s00381-023-06081-1. Epub 2023 Oct 13. Childs Nerv Syst. 2023. PMID: 37831207 Review.
-
Pituitary stalk thickening in patients under 18 years of age - the most common causes and diagnostic procedures.Pediatr Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2022;28(3):213-227. doi: 10.5114/pedm.2022.115202. Pediatr Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2022. PMID: 35620922 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Significance of human chorionic gonadotropin as a predictor of resistance to standard chemo-radiotherapy for pure germinoma.Neurosurg Rev. 2018 Apr;41(2):557-565. doi: 10.1007/s10143-017-0891-3. Epub 2017 Aug 18. Neurosurg Rev. 2018. PMID: 28819802
-
LncRNA SNHG5 Promotes Proliferation of Glioma by Regulating miR-205-5p/ZEB2 Axis.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Dec 27;12:11487-11496. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S228439. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 31920337 Free PMC article.
-
A Craniopharyngioma Associated With Elevated Cerebrospinal Fluid HCG Concentrations Misdiagnosed as a Germinoma.Front Neurol. 2018 Jun 14;9:449. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2018.00449. eCollection 2018. Front Neurol. 2018. PMID: 29963005 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cho KT, Wang KC, Kim SK, Shin SH, Chi JG, Cho BK. Pediatric brain tumors: Statistics of SNUH, Korea (1959–2000). Childs Nerv Syst. 2002;18: 30–37. - PubMed
-
- Jennings MT, Gelman R, Hochberg F. Intracranial germ-cell tumors: natural history and pathogenesis. J Neurosurg. 1985;63: 155–167. - PubMed
-
- Paulino AC, Wen BC, Mohideen MN. Controversies in the management of intracranial germinomas. Oncology (Williston Park). 1999;13: 513–521; discussion 521–522, 528–523. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical