Protection against Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation/Reperfusion Injury in Cortical Neurons by Combining Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Acid with Lyciumbarbarum Polysaccharide
- PMID: 26771636
- PMCID: PMC4728654
- DOI: 10.3390/nu8010041
Protection against Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation/Reperfusion Injury in Cortical Neurons by Combining Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Acid with Lyciumbarbarum Polysaccharide
Abstract
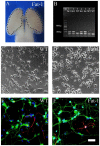
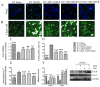
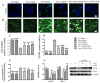
Ischemic stroke, characterized by the disturbance of the blood supply to the brain, is a severe worldwide health threat with high mortality and morbidity. However, there is no effective pharmacotherapy for ischemic injury. Currently, combined treatment is highly recommended for this devastating injury. In the present study, we investigated neuroprotective effects of the combination of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (ω-3 PUFAs) and Lyciumbarbarum polysaccharide (LBP) on cortical neurons using an in vitro ischemic model. Our study demonstrated that treatment with docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), a major component of the ω-3 PUFAs family, significantly inhibited the increase of intracellular Ca(2+) in cultured wild type (WT) cortical neurons subjected to oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion (OGD/R) injury and promoted their survival compared with the vehicle-treated control. The protective effects were further confirmed in cultured neurons with high endogenous ω-3 PUFAs that were isolated from fat-1 mice, in that a higher survival rate was found in fat-1 neurons compared with wild-type neurons after OGD/R injury. Our study also found that treatment with LBP (50 mg/L) activated Trk-B signaling in cortical neurons and significantly attenuated OGD/R-induced cell apoptosis compared with the control. Notably, both combining LBP treatment with ω-3 PUFAs administration to WT neurons and adding LBP to fat-1 neurons showed enhanced effects on protecting cortical neurons against OGD/R injury via concurrently regulating the intracellular calcium overload and neurotrophic pathway. The results of the study suggest that ω-3 PUFAs and LBP are promising candidates for combined pharmacotherapy for ischemic stroke.
Keywords: Ca2+; DHA; LBP; OGD/R; Trk-B; cortical neurons; neuroprotection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enriched Endogenous Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Protect Cortical Neurons from Experimental Ischemic Injury.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Nov;53(9):6482-6488. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9554-y. Epub 2015 Nov 26. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26611833
-
Lycium barbarum polysaccharide protects against oxygen glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis and autophagic cell death via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in primary cultured hippocampal neurons.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Jan 1;495(1):1187-1194. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.11.165. Epub 2017 Nov 26. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 29183728
-
Neuroprotective effects of syringic acid against OGD/R-induced injury in cultured hippocampal neuronal cells.Int J Mol Med. 2016 Aug;38(2):567-73. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2623. Epub 2016 Jun 3. Int J Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27278454
-
An In Vitro Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation Model for Studying Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury of Neuronal Cells.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1717:229-235. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7526-6_18. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29468596 Review.
-
Post-stroke administration of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids promotes neurovascular restoration after ischemic stroke in mice: Efficacy declines with aging.Neurobiol Dis. 2019 Jun;126:62-75. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2018.09.012. Epub 2018 Sep 12. Neurobiol Dis. 2019. PMID: 30218758 Review.
Cited by
-
Blockade of L-Type Ca2+ Channel Activity Alleviates Oligodendrocyte Pathology following Brain Injury in Male Rats.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 May 2;45(5):3953-3964. doi: 10.3390/cimb45050252. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37232721 Free PMC article.
-
Effects and mechanism of dexmedetomidine on neuronal cell injury induced by hypoxia-ischemia.BMC Anesthesiol. 2017 Aug 30;17(1):117. doi: 10.1186/s12871-017-0413-4. BMC Anesthesiol. 2017. PMID: 28854873 Free PMC article.
-
Cannabidiol attenuates OGD/R-induced damage by enhancing mitochondrial bioenergetics and modulating glucose metabolism via pentose-phosphate pathway in hippocampal neurons.Redox Biol. 2017 Apr;11:577-585. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2016.12.029. Epub 2016 Dec 31. Redox Biol. 2017. PMID: 28110213 Free PMC article.
-
Die Hard: Necroptosis and its Impact on Age-Dependent Neuroinflammatory Diseases.Front Cell Death. 2024;3:1348153. doi: 10.3389/fceld.2024.1348153. Epub 2024 Mar 8. Front Cell Death. 2024. PMID: 40741039 Free PMC article.
-
Lycium barbarum polysaccharides inhibit ischemia/reperfusion-induced myocardial injury via the Nrf2 antioxidant pathway.Toxicol Rep. 2021 Mar 24;8:657-667. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2021.03.019. eCollection 2021. Toxicol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33868952 Free PMC article.
References
-
- O’Collins V.E., Macleod M.R., Donnan G.A., Horky L.L., van der Worp B.H., Howells D.W. 1026 experimental treatments in acute stroke. Ann. Neurol. 2006;59:467–477. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

