The Effect of Co-Administration of Death Camas (Zigadenus spp.) and Low Larkspur (Delphinium spp.) in Cattle
- PMID: 26771639
- PMCID: PMC4728543
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins8010021
The Effect of Co-Administration of Death Camas (Zigadenus spp.) and Low Larkspur (Delphinium spp.) in Cattle
Abstract
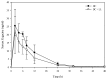
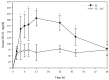
In many rangeland settings, there is more than one potential poisonous plant. Two poisonous plants that are often found growing simultaneously in the same location in North American rangelands are death camas (Zigadenus spp.) and low larkspur (Delphinium spp.). The objective of this study was to determine if co-administration of death camas would exacerbate the toxicity of low larkspur in cattle. Cattle dosed with 2.0 g of death camas/kg BW showed slight frothing and lethargy, whereas cattle dosed with both death camas and low larkspur showed increased clinical signs of poisoning. Although qualitative differences in clinical signs of intoxication in cattle co-treated with death camas and low larkspur were observed, there were not any significant quantitative differences in heart rate or exercise-induced muscle fatigue. Co-treatment with death camas and low larkspur did not affect the serum zygacine kinetics, however, there was a difference in the larkspur alkaloid kinetics in the co-exposure group. Overall, the results from this study suggest that co-exposure to death camas and low larkspur is not significantly more toxic to cattle than exposure to the plants individually. The results from this study increase our knowledge and understanding regarding the acute toxicity of death camas and low larkspur in cattle.
Keywords: Delphinium; Zigadenus; cattle; death camas; larkspur; methyllycaconitine; zygacine.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The effect of low larkspur (Delphinium spp.) co-administration on the acute toxicity of death camas (Zigadenus spp.) in sheep.Toxicon. 2013 Dec 15;76:50-8. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2013.09.007. Epub 2013 Sep 18. Toxicon. 2013. PMID: 24055068
-
The acute toxicity of the death camas (Zigadenus species) alkaloid zygacine in mice, including the effect of methyllycaconitine coadministration on zygacine toxicity.J Anim Sci. 2011 May;89(5):1650-7. doi: 10.2527/jas.2010-3444. J Anim Sci. 2011. PMID: 21521823
-
Analysis of rumen contents and ocular fluid for toxic alkaloids from goats and cows dosed larkspur (Delphinium barbeyi), lupine (Lupinus leucophyllus), and death camas (Zigadenus paniculatus).Toxicon. 2020 Mar;176:21-29. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2020.01.003. Epub 2020 Jan 11. Toxicon. 2020. PMID: 31965970
-
Larkspur (Delphinium spp.) poisoning in livestock.J Nat Toxins. 1999 Feb;8(1):81-94. J Nat Toxins. 1999. PMID: 10091130 Review.
-
Plant-animal interactions in larkspur poisoning in cattle.J Anim Sci. 1988 Sep;66(9):2334-42. doi: 10.2527/jas1988.6692334x. J Anim Sci. 1988. PMID: 3049494 Review.
References
-
- Panter K.E., Ralphs M.H., Smart R.A., Duelke B. Death camas poisoning in sheep: A case report. Vet. Hum. Toxicol. 1987;29:45–48. - PubMed
-
- Kingsbury J.M. Poisonous Plants of the United States and Canada. Prentice-Hall, Inc.; Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA: 1964.
-
- Smith R.A., Lewis D. Death camas poisoning in cattle. Vet. Hum. Toxicol. 1991;33:615–616. - PubMed
-
- Collet S.D., Grotelueschen D., Smith R., Wilson R. Deaths of 23 adult cows attributed to intoxication by the alkaloids of Zigadenus venosus (meadow death camas) Agric. Practice. 1996;17:5–9.
-
- Knight A.P., Walter R.G. A Guide to Plant Poisoning of Animals in North America. Teton New Media; Jackson Hole, WY, USA: 2001.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

