Facilitation of axon outgrowth via a Wnt5a-CaMKK-CaMKIα pathway during neuronal polarization
- PMID: 26772170
- PMCID: PMC4715351
- DOI: 10.1186/s13041-016-0189-3
Facilitation of axon outgrowth via a Wnt5a-CaMKK-CaMKIα pathway during neuronal polarization
Abstract
Background: Wnt5a, originally identified as a guidance cue for commissural axons, activates a non-canonical pathway critical for cortical axonal morphogenesis. The molecular signaling cascade underlying this event remains obscure.
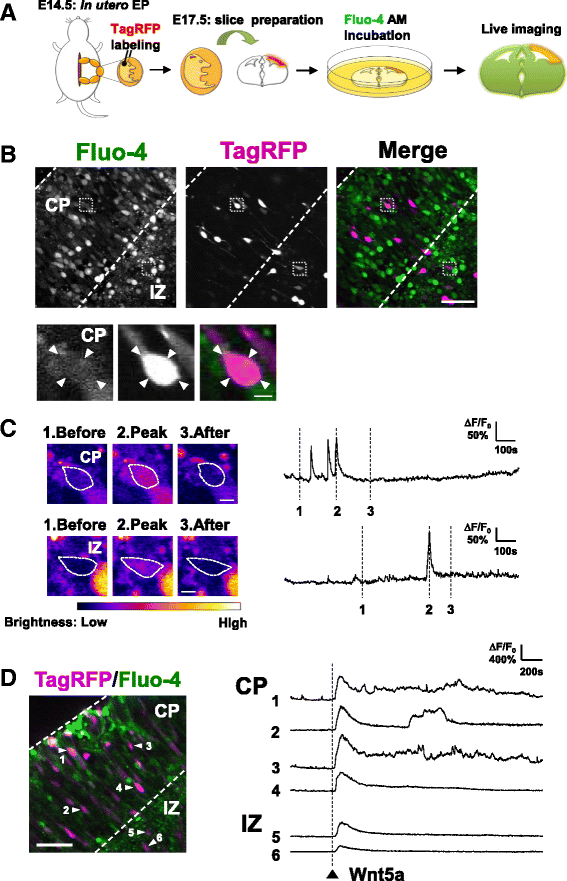
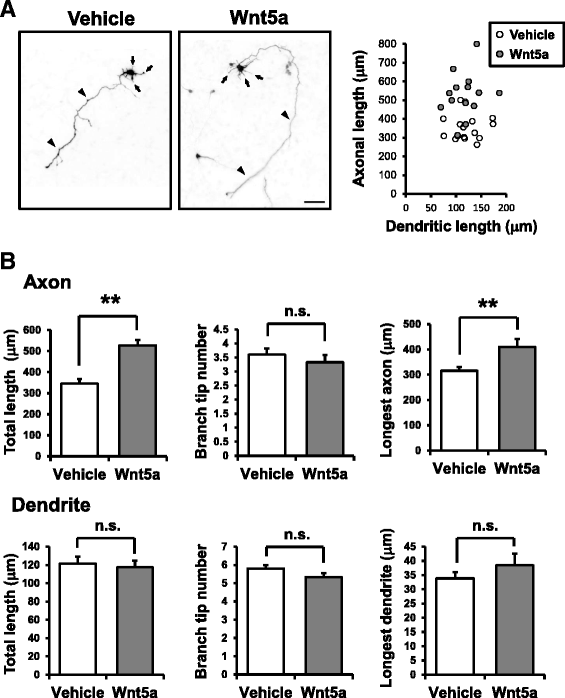
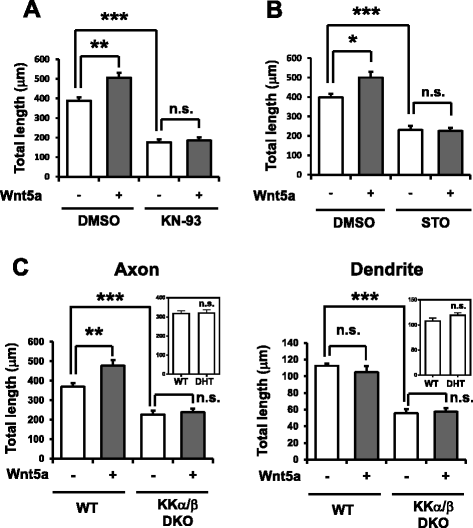
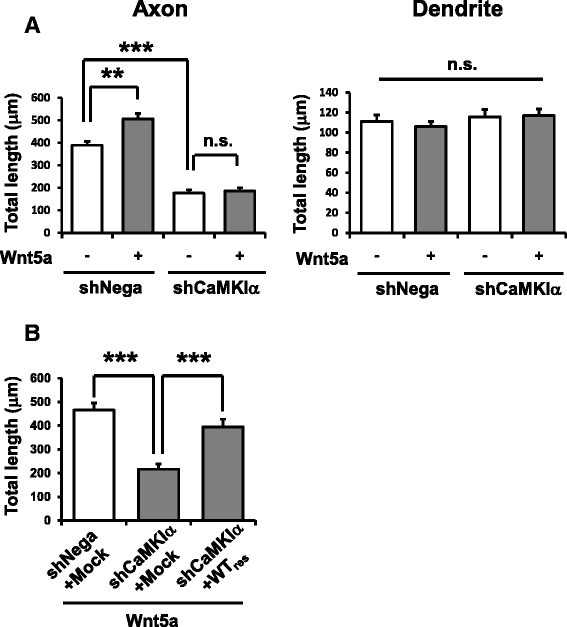
Results: Through Ca(2+) imaging in acute embryonic cortical slices, we tested if radially migrating cortical excitatory neurons that already bore primitive axons were sensitive to Wnt5a. While Wnt5a only evoked brief Ca(2+) transients in immature neurons present in the intermediate zone (IZ), Wnt5a-induced Ca(2+) oscillations were sustained in neurons that migrated out to the cortical plate (CP). We wondered whether this early Wnt5a-Ca(2+) signaling during neuronal polarization has a morphogenetic consequence. During transition from round to polarized shape, Wnt5a administration to immature cultured cortical neurons specifically promoted axonal, but not dendritic, outgrowth. Pharmacological and genetic inhibition of the CaMKK-CaMKIα pathway abolished Wnt5a-induced axonal elongation, and rescue of CaMKIα in CaMKIα-knockdown neurons restored Wnt5a-mediated axon outgrowth.
Conclusions: This study suggests that Wnt5a activates Ca(2+) signaling during a neuronal morphogenetic time window when axon outgrowth is critically facilitated. Furthermore, the CaMKK-CaMKIα cascade is required for the axonal growth effect of Wnt5a during neuronal polarization.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Control of cortical axon elongation by a GABA-driven Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase cascade.J Neurosci. 2009 Oct 28;29(43):13720-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3018-09.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19864584 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt5a induces Ryk-dependent and -independent effects on callosal axon and dendrite growth.Growth Factors. 2014 Feb;32(1):11-7. doi: 10.3109/08977194.2013.875544. Growth Factors. 2014. PMID: 24471468
-
Transient receptor potential canonical 5 channels activate Ca2+/calmodulin kinase Igamma to promote axon formation in hippocampal neurons.J Neurosci. 2009 Aug 5;29(31):9794-808. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1544-09.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19657032 Free PMC article.
-
CaMKK-CaMKI signaling pathways differentially control axon and dendrite elongation in cortical neurons.J Neurosci. 2010 Feb 24;30(8):2807-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5984-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20181577 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Wnt5a: its signalling, functions and implication in diseases.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2012 Jan;204(1):17-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.2011.02294.x. Epub 2011 Apr 22. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2012. PMID: 21518267 Review.
Cited by
-
Chd5 Regulates the Transcription Factor Six3 to Promote Neuronal Differentiation.Stem Cells. 2023 Mar 17;41(3):242-251. doi: 10.1093/stmcls/sxad002. Stem Cells. 2023. PMID: 36636025 Free PMC article.
-
A Role for Second Messengers in Axodendritic Neuronal Polarity.J Neurosci. 2023 Mar 22;43(12):2037-2052. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1065-19.2023. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36948585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Ca2+/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase Kinase Signal Transduction.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 20;23(19):11025. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911025. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232320 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AMP-activated protein kinase-mediated feedback phosphorylation controls the Ca2+/calmodulin (CaM) dependence of Ca2+/CaM-dependent protein kinase kinase β.J Biol Chem. 2017 Dec 1;292(48):19804-19813. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.805085. Epub 2017 Oct 3. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28974582 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt5a Promotes Axon Elongation in Coordination with the Wnt-Planar Cell Polarity Pathway.Cells. 2024 Jul 28;13(15):1268. doi: 10.3390/cells13151268. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39120298 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

