Target Identification in Small Cell Lung Cancer via Integrated Phenotypic Screening and Activity-Based Protein Profiling
- PMID: 26772203
- PMCID: PMC4747823
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-0444
Target Identification in Small Cell Lung Cancer via Integrated Phenotypic Screening and Activity-Based Protein Profiling
Abstract
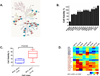
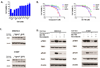
To overcome hurdles in identifying key kinases in small cell lung cancer (SCLC), we integrated a target-agnostic phenotypic screen of kinase inhibitors with target identification using activity-based protein profiling (ABPP) in which a desthiobiotin-ATP probe was used. We screened 21 SCLC cell lines with known c-MYC amplification status for alterations in viability using a chemical library of 235 small-molecule kinase inhibitors. One screen hit compound was interrogated with ABPP, and, through this approach, we reidentified Aurora kinase B as a critical kinase in MYC-amplified SCLC cells. We next extended the platform to a second compound that had activity in SCLC cell lines lacking c-MYC amplification and identified TANK-binding kinase 1, a kinase that affects cell viability, polo-like kinase-1 signaling, G2-M arrest, and apoptosis in SCLC cells lacking MYC amplification. These results demonstrate that phenotypic screening combined with ABPP can identify key disease drivers, suggesting that this approach, which combines new chemical probes and disease cell screens, has the potential to identify other important targets in other cancer types. Mol Cancer Ther; 15(2); 334-42. ©2016 AACR.
©2016 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
An integrated genomic approach to identify predictive biomarkers of response to the aurora kinase inhibitor PF-03814735.Mol Cancer Ther. 2012 Mar;11(3):710-9. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0184. Epub 2012 Jan 5. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012. PMID: 22222631
-
Barasertib (AZD1152), a Small Molecule Aurora B Inhibitor, Inhibits the Growth of SCLC Cell Lines In Vitro and In Vivo.Mol Cancer Ther. 2016 Oct;15(10):2314-2322. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-16-0298. Epub 2016 Aug 5. Mol Cancer Ther. 2016. PMID: 27496133 Free PMC article.
-
A framework for identification of actionable cancer genome dependencies in small cell lung cancer.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Oct 16;109(42):17034-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1207310109. Epub 2012 Oct 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23035247 Free PMC article.
-
Family matters: How MYC family oncogenes impact small cell lung cancer.Cell Cycle. 2017 Aug 18;16(16):1489-1498. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2017.1339849. Epub 2017 Jul 24. Cell Cycle. 2017. PMID: 28737478 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Seeking New Approaches to Patients With Small Cell Lung Cancer.Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2016;35:e477-82. doi: 10.1200/EDBK_158710. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2016. PMID: 27249756 Review.
Cited by
-
Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote Gastric Cancer Growth via Regulating c-Myc.Stem Cells Int. 2018 Jul 18;2018:9501747. doi: 10.1155/2018/9501747. eCollection 2018. Stem Cells Int. 2018. PMID: 30186330 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical Probes and Activity-Based Protein Profiling for Cancer Research.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 25;23(11):5936. doi: 10.3390/ijms23115936. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35682614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Senotherapeutics in Cancer and HIV.Cells. 2022 Apr 4;11(7):1222. doi: 10.3390/cells11071222. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35406785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of Quantitative Mass Spectrometry Platforms for Monitoring Kinase ATP Probe Uptake in Lung Cancer.J Proteome Res. 2018 Jan 5;17(1):63-75. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.7b00329. Epub 2017 Nov 22. J Proteome Res. 2018. PMID: 29164889 Free PMC article.
-
Divergent Polypharmacology-Driven Cellular Activity of Structurally Similar Multi-Kinase Inhibitors through Cumulative Effects on Individual Targets.Cell Chem Biol. 2019 Sep 19;26(9):1240-1252.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2019.06.003. Epub 2019 Jun 27. Cell Chem Biol. 2019. PMID: 31257184 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rix U, Superti-Furga G. Target profiling of small molecules by chemical proteomics. Nat Chem Biol. 2009;5:616–624. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

