Assessing variability in results in systematic reviews of diagnostic studies
- PMID: 26772804
- PMCID: PMC4714528
- DOI: 10.1186/s12874-016-0108-4
Assessing variability in results in systematic reviews of diagnostic studies
Abstract
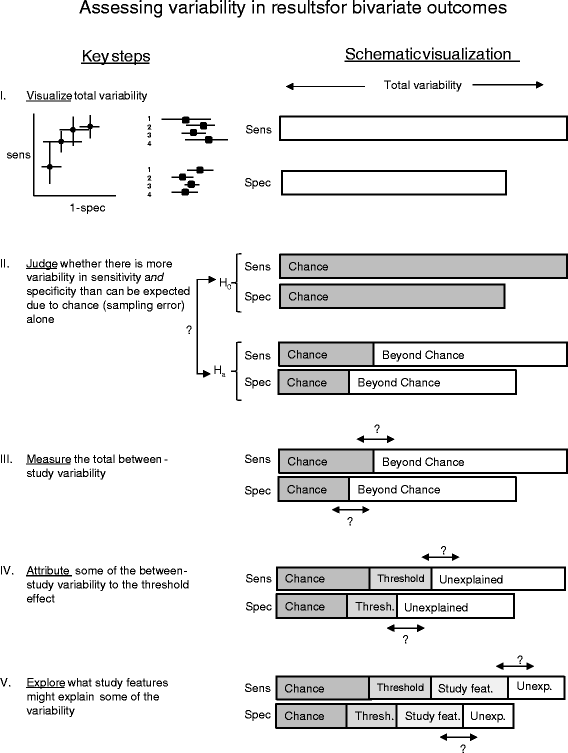
Background: To describe approaches used in systematic reviews of diagnostic test accuracy studies for assessing variability in estimates of accuracy between studies and to provide guidance in this area.
Methods: Meta-analyses of diagnostic test accuracy studies published between May and September 2012 were systematically identified. Information on how the variability in results was investigated was extracted.
Results: Of the 53 meta-analyses included in the review, most (n=48; 91%) presented variability in diagnostic accuracy estimates visually either through forest plots or ROC plots and the majority (n=40; 75%) presented a test or statistical measure for the variability. Twenty-eight reviews (53%) tested for variability beyond chance using Cochran's Q test and 31 (58%) reviews quantified it with I(2). 7 reviews (13%) presented between-study variance estimates (τ(2)) from random effects models and 3 of these presented a prediction interval or ellipse to facilitate interpretation. Half of all the meta-analyses specified what was considered a significant amount of variability (n=24; 49%).
Conclusions: Approaches to assessing variability in estimates of accuracy varied widely between diagnostic test accuracy reviews and there is room for improvement. We provide initial guidance, complemented by an overview of the currently available approaches.
Figures
References
-
- Dahabreh IJ, Chung M, Kitsios GD, Teruhiko T, Raman G, Tatsioni A, et al. Comprehensive Overview of Methods and Reporting of Meta-Analyses of Test Accuracy. Rockville: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2012. - PubMed
-
- Deeks J, Bossuyt P, Gatsonis C. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Diagnostic Test Accuracy Version 1.0 (Chapter 10). 2010.
-
- Borenstein M, Hedges LV, Higgins JP, Rothstein HR. Introduction to Meta-Analysis. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons; 2009.
-
- Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Chichester: Wiley-Blackwell; 2008.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical