Red Raspberries and Their Bioactive Polyphenols: Cardiometabolic and Neuronal Health Links
- PMID: 26773014
- PMCID: PMC4717884
- DOI: 10.3945/an.115.009639
Red Raspberries and Their Bioactive Polyphenols: Cardiometabolic and Neuronal Health Links
Abstract
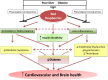
Diet is an essential factor that affects the risk of modern-day metabolic diseases, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, obesity, and Alzheimer disease. The potential ability of certain foods and their bioactive compounds to reverse or prevent the progression of the pathogenic processes that underlie these diseases has attracted research attention. Red raspberries (Rubus idaeus L.) are unique berries with a rich history and nutrient and bioactive composition. They possess several essential micronutrients, dietary fibers, and polyphenolic components, especially ellagitannins and anthocyanins, the latter of which give them their distinctive red coloring. In vitro and in vivo studies have revealed various mechanisms through which anthocyanins and ellagitannins (via ellagic acid or their urolithin metabolites) and red raspberry extracts (or the entire fruit) could reduce the risk of or reverse metabolically associated pathophysiologies. To our knowledge, few studies in humans are available for evaluation. We review and summarize the available literature that assesses the health-promoting potential of red raspberries and select components in modulating metabolic disease risk, especially cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, obesity, and Alzheimer disease-all of which share critical metabolic, oxidative, and inflammatory links. The body of research is growing and supports a potential role for red raspberries in reducing the risk of metabolically based chronic diseases.
Keywords: anthocyanins; cardiovascular disease; diabetes; ellagic acid; inflammation; oxidative stress; polyphenols; red raspberries.
© 2016 American Society for Nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
Author disclosures: BM Burton-Freeman, AK Sandhu, and I Edirisinghe, no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- USDA. Scientific report of the 2015 Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee. Washington (DC): USDA; 2015. [cited 2015 Jan 2]. Available from: http://www.health.gov/dietaryguidelines/2015-scientific-report/PDFs/Scie.... - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hunter C. Raspberry history, folklore, myth, and magic. The Practical Herbalist [Internet] [cited 2015 May 3]. Available from: http://www.thepracticalherbalist.com/herbal-library/magical-herbs/raspbe....
-
- Rayment WJ. Raspberry history. InDepthInfo [Internet]. [cited 2014 Aug 10]. Available from: http://www.indepthinfo.com/raspberries/history.htm.
-
- Washington Red Raspberry Commission. History. Lynden (WA): Washington Red Raspberry Commission; 2013. [cited 2014 May 6]. Available from: http://www.red-raspberry.org/history.asp.
-
- USDA. National Agriculture Statistics Service Quick Stats 2.0 [Internet] [cited 2014 Jul 17]. Available from: http://www.nass.usda.gov/Quick_Stats.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

