Physiology of Food Intake Control in Children
- PMID: 26773031
- PMCID: PMC4717882
- DOI: 10.3945/an.115.009357
Physiology of Food Intake Control in Children
Abstract
The purpose of this review is to draw attention to the limited information available on food intake (FI) control in children and adolescents 7-17 y of age, which is essential for developing food policies and guidelines in this population. Although environmental factors have been the overwhelming focus of research on the causative factors of obesity, research focusing on the physiologic control of appetite in children and adolescents is a neglected area of research. To present this message, a review of FI regulation and the role of food and food components in signaling processes are followed by an examination of the role of hormones during puberty in intake regulation. To examine the interaction of environment and physiology on FI regulation, the effects of exercise, television programs, and food advertisements are discussed. In conclusion, although limited, this literature review supports a need for children and adolescents to be a greater focus of research that would lead to sound nutrition policies and actions to reduce chronic disease. A focus on the environment must be balanced with an understanding of physiologic and behavioral changes associated with this age group.
Keywords: children; food advertisements; food intake regulation; hormones; macronutrients; physical activity; puberty.
© 2016 American Society for Nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
Author disclosures. GH Anderson, S Hunschede, R Akilen, and R Kubant, no conflicts of interest.
Figures

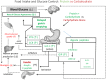
Similar articles
-
Beyond-brand effect of television food advertisements on food choice in children: the effects of weight status.Public Health Nutr. 2008 Sep;11(9):897-904. doi: 10.1017/S1368980007001231. Epub 2007 Nov 16. Public Health Nutr. 2008. PMID: 18005487 Clinical Trial.
-
Watching television or listening to music while exercising failed to affect post-exercise food intake or energy expenditure in male adolescents.Appetite. 2018 Aug 1;127:266-273. doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2018.05.016. Epub 2018 May 14. Appetite. 2018. PMID: 29772291 Clinical Trial.
-
Pubertal status, pre-meal drink composition, and later meal timing interact in determining children's appetite and food intake.Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2016 Sep;41(9):924-30. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2016-0079. Epub 2016 Apr 26. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2016. PMID: 27507005 Clinical Trial.
-
Understanding the mechanisms of food intake and obesity.Obes Rev. 2007 Mar;8 Suppl 1:67-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-789X.2007.00321.x. Obes Rev. 2007. PMID: 17316305 Review. No abstract available.
-
Development of eating behaviors among children and adolescents.Pediatrics. 1998 Mar;101(3 Pt 2):539-49. Pediatrics. 1998. PMID: 12224660 Review.
Cited by
-
Mealtime media use and cardiometabolic risk in children.Public Health Nutr. 2022 Mar;25(3):670-679. doi: 10.1017/S1368980020003821. Epub 2020 Dec 2. Public Health Nutr. 2022. PMID: 33263271 Free PMC article.
-
The complex relationship between diet, quality of life and life expectancy: a narrative review of potential determinants based on data from Italy.Eat Weight Disord. 2019 Jun;24(3):411-419. doi: 10.1007/s40519-018-0582-2. Epub 2018 Sep 27. Eat Weight Disord. 2019. PMID: 30264391 Review.
-
Multi-etiological Perspective on Child Obesity Prevention.Curr Nutr Rep. 2019 Jan 16:10.1007/s13668-019-0256-3. doi: 10.1007/s13668-019-0256-3. Online ahead of print. Curr Nutr Rep. 2019. PMID: 30649714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Next Steps for Science and Policy on Promoting Vegetable Consumption among US Infants and Young Children.Adv Nutr. 2016 Jan 15;7(1):261S-271S. doi: 10.3945/an.115.009332. Print 2016 Jan. Adv Nutr. 2016. PMID: 26773035 Free PMC article.
-
Consumption Patterns of Sugar-Sweetened Beverages and Association with Undernutrition among Children Aged 9-17 Years in Guangzhou, China: A Cross-Sectional Study.Nutrients. 2024 Feb 26;16(5):650. doi: 10.3390/nu16050650. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38474778 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ebbeling CB, Sinclair KB, Pereira MA, Garcia-Lago E, Feldman HA, Ludwig DS. Compensation for energy intake from fast food among overweight and lean adolescents. JAMA 2004;291:2828–33. - PubMed
-
- Hill JO, Wyatt HR, Reed GW, Peters JC. Obesity and the environment: where do we go from here? Science 2003;299:853–5. - PubMed
-
- Wansink B. Environmental factors that increase the food intake and consumption volume of unknowing consumers. Annu Rev Nutr 2004;24:455–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

