Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patient-derived xenograft models capture the molecular and biological heterogeneity of the disease
- PMID: 26773040
- PMCID: PMC4859195
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2015-09-672352
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patient-derived xenograft models capture the molecular and biological heterogeneity of the disease
Abstract
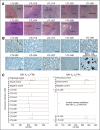
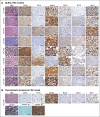
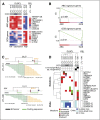
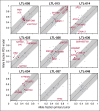
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is a heterogeneous disease defined by transcriptional classifications, specific signaling and survival pathways, and multiple low-frequency genetic alterations. Preclinical model systems that capture the genetic and functional heterogeneity of DLBCL are urgently needed. Here, we generated and characterized a panel of large B-cell lymphoma (LBCL) patient-derived xenograft (PDX) models, including 8 that reflect the immunophenotypic, transcriptional, genetic, and functional heterogeneity of primary DLBCL and 1 that is a plasmablastic lymphoma. All LBCL PDX models were subjected to whole-transcriptome sequencing to classify cell of origin and consensus clustering classification (CCC) subtypes. Mutations and chromosomal rearrangements were evaluated by whole-exome sequencing with an extended bait set. Six of the 8 DLBCL models were activated B-cell (ABC)-type tumors that exhibited ABC-associated mutations such as MYD88, CD79B, CARD11, and PIM1. The remaining 2 DLBCL models were germinal B-cell type, with characteristic alterations of GNA13, CREBBP, and EZH2, and chromosomal translocations involving IgH and either BCL2 or MYC Only 25% of the DLBCL PDX models harbored inactivating TP53 mutations, whereas 75% exhibited copy number alterations of TP53 or its upstream modifier, CDKN2A, consistent with the reported incidence and type of p53 pathway alterations in primary DLBCL. By CCC criteria, 6 of 8 DLBCL PDX models were B-cell receptor (BCR)-type tumors that exhibited selective surface immunoglobulin expression and sensitivity to entospletinib, a recently developed spleen tyrosine kinase inhibitor. In summary, we have established and characterized faithful PDX models of DLBCL and demonstrated their usefulness in functional analyses of proximal BCR pathway inhibition.
© 2016 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures
References
-
- Freedman AS, Friedberg JW, Aster JC. Classification of the hematopoietic neoplasms. Available at: www.uptodate.com/contents/classification-of-the-hematopoietic-neoplasms?.... Accessed August 9, 2015.
-
- Monti S, Savage KJ, Kutok JL, et al. Molecular profiling of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identifies robust subtypes including one characterized by host inflammatory response. Blood. 2005;105(5):1851–1861. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

