Cutting Edge: CD99 Is a Novel Therapeutic Target for Control of T Cell-Mediated Central Nervous System Autoimmune Disease
- PMID: 26773145
- PMCID: PMC4744533
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1501634
Cutting Edge: CD99 Is a Novel Therapeutic Target for Control of T Cell-Mediated Central Nervous System Autoimmune Disease
Abstract
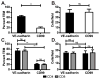
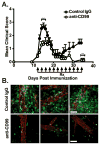
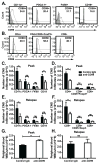
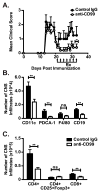
Leukocyte trafficking into the CNS is a prominent feature driving the immunopathogenesis of multiple sclerosis and its animal model, experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Blocking the recruitment of inflammatory leukocytes into the CNS represents an exploitable therapeutic target; however, the adhesion molecules that specifically regulate the step of leukocyte diapedesis into the CNS remain poorly understood. We report that CD99 is critical for lymphocyte transmigration without affecting adhesion in a human blood-brain barrier model. CD99 blockade in vivo ameliorated experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and decreased the accumulation of CNS inflammatory infiltrates, including dendritic cells, B cells, and CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells. Anti-CD99 therapy was effective when administered after the onset of disease symptoms and blocked relapse when administered therapeutically after disease symptoms had recurred. These findings underscore an important role for CD99 in the pathogenesis of CNS autoimmunity and suggest that it may serve as a novel therapeutic target for controlling neuroinflammation.
Copyright © 2016 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Beneficial effect of modified peptide inhibitor of alpha4 integrins on experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in Lewis rats.J Neurosci Res. 2002 Jan 15;67(2):191-9. doi: 10.1002/jnr.10095. J Neurosci Res. 2002. PMID: 11782963
-
Depletion of CD52-positive cells inhibits the development of central nervous system autoimmune disease, but deletes an immune-tolerance promoting CD8 T-cell population. Implications for secondary autoimmunity of alemtuzumab in multiple sclerosis.Immunology. 2017 Apr;150(4):444-455. doi: 10.1111/imm.12696. Epub 2017 Jan 3. Immunology. 2017. PMID: 27925187 Free PMC article.
-
Cell surface levels of endothelial ICAM-1 influence the transcellular or paracellular T-cell diapedesis across the blood-brain barrier.Eur J Immunol. 2015 Apr;45(4):1043-58. doi: 10.1002/eji.201445125. Epub 2015 Jan 23. Eur J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25545837
-
Emerging concepts in autoimmune encephalomyelitis beyond the CD4/T(H)1 paradigm.Ann Anat. 2010 Aug 20;192(4):179-93. doi: 10.1016/j.aanat.2010.06.006. Epub 2010 Jul 15. Ann Anat. 2010. PMID: 20692821 Review.
-
The role of CD8 suppressors versus destructors in autoimmune central nervous system inflammation.Hum Immunol. 2008 Nov;69(11):797-804. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2008.07.014. Epub 2008 Aug 22. Hum Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18723060 Review.
Cited by
-
Escape from X chromosome inactivation and female bias of autoimmune diseases.Mol Med. 2020 Dec 9;26(1):127. doi: 10.1186/s10020-020-00256-1. Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 33297945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure and Junctional Complexes of Endothelial, Epithelial and Glial Brain Barriers.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 29;20(21):5372. doi: 10.3390/ijms20215372. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31671721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acetylcholine-producing NK cells attenuate CNS inflammation via modulation of infiltrating monocytes/macrophages.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Jul 25;114(30):E6202-E6211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1705491114. Epub 2017 Jul 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28696300 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the Mysteries of the Blood-brain Barrier: The Problem of the Brain/spinal Pharmacotherapy.Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2025;25(2):91-108. doi: 10.2174/0118715249297247240813104929. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39206486 Review.
-
Clofarabine inhibits Ewing sarcoma growth through a novel molecular mechanism involving direct binding to CD99.Oncogene. 2018 Apr;37(16):2181-2196. doi: 10.1038/s41388-017-0080-4. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Oncogene. 2018. PMID: 29382926 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hickey WF. Basic principles of immunological surveillance of the normal central nervous system. Glia. 2001;36:118–124. - PubMed
-
- Frohman EM, Racke MK, Raine CS. Multiple sclerosis--the plaque and its pathogenesis. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:942–955. - PubMed
-
- Lucchinetti C, Bruck W, Parisi J, Scheithauer B, Rodriguez M, Lassmann H. Heterogeneity of multiple sclerosis lesions: implications for the pathogenesis of demyelination. Annals of neurology. 2000;47:707–717. - PubMed
-
- Ifergan I, Kebir H, Bernard M, Wosik K, Dodelet-Devillers A, Cayrol R, Arbour N, Prat A. The blood-brain barrier induces differentiation of migrating monocytes into Th17-polarizing dendritic cells. Brain: a journal of neurology. 2008;131:785–799. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

