Histopathology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
- PMID: 26775559
- PMCID: PMC4889547
- DOI: 10.1016/j.metabol.2015.11.008
Histopathology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
Abstract
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the liver injury most often associated with disorders of insulin resistance, including obesity, diabetes and the metabolic syndrome. The term encompasses several patterns of liver injury, including a relatively benign condition of steatosis without hepatocellular injury, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), and a pattern of zone 1 steatosis, inflammation and fibrosis mainly observed in prepubertal children. Staging and grading systems have been developed to characterize the histological changes in NAFLD, mainly as a tool for clinical research. The histological features of NAFLD across these different manifestations and the scoring systems used to evaluate disease severity are discussed.
Keywords: Histology; Liver biopsy; Steatohepatitis; Steatosis.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
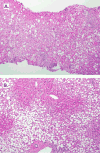
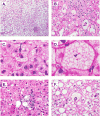

References
-
- d’Assignies G, Fontes G, Kauffmann C, Latour M, Gaboury L, Boulanger Y, Van Beers BE, Soulez G, Poitout V, Tang A. Early detection of liver steatosis by magnetic resonance imaging in rats infused with glucose and intralipid solutions and correlation to insulin levels. Metabolism. 2013;62:1850–1857. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Adams LA, Ratziu V. Non-alcoholic fatty liver - perhaps not so benign. Journal of hepatology. 2015;62:1002–1004. - PubMed
-
- Argo CK, Caldwell SH. Epidemiology and natural history of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Clinics in liver disease. 2009;13:511–531. - PubMed
-
- Starley BQ, Calcagno CJ, Harrison SA. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma: a weighty connection. Hepatology. 2010;51:1820–1832. - PubMed
-
- Karagozian R, Derdak Z, Baffy G. Obesity-associated mechanisms of hepatocarcinogenesis. Metabolism. 2014;63:607–617. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

