Effect of ready-to-use foods for preventing child undernutrition in Niger: analysis of a prospective intervention study over 15 months of follow-up
- PMID: 26775560
- PMCID: PMC6866220
- DOI: 10.1111/mcn.12236
Effect of ready-to-use foods for preventing child undernutrition in Niger: analysis of a prospective intervention study over 15 months of follow-up
Abstract
Strategies for preventing undernutrition comprise a range of interventions, including education, provision of complementary food and cash transfer. Here, we compared monthly distributions of two different lipid-based nutrient supplements (LNS), large-quantity LNS (LNS-LQ) and medium-quantity LNS (LNS-MQ) for 15 months on prevention of undernutrition among children 6 to 23 months. Both groups also received cash transfer for the first 5 months of the intervention. We conducted a prospective intervention study in Maradi, Niger, between August 2011 and October 2012. Six and 11 villages were randomly allocated to LNS-LQ/Cash and LNS-MQ/Cash, respectively. Children measuring 60-80 cm were enrolled in the respective groups and followed up monthly. Poisson regression was used to assess differences between interventions and adjust for baseline characteristics, intervention periods and child-feeding practices. The analysis included 2586 children (1081 in the LNS-LQ/Cash group and 1505 in the LNS-MQ/Cash group). This study suggests that provision of LNS-LQ (reference) or LNS-MQ had, overall, similar effect on incidence of severe acute malnutrition (RR = 0.97; 95% CI: 0.67-1.40; P = 0.88), moderate acute malnutrition (RR = 1.20; 95% CI: 0.97-1.48; P = 0.08), severe stunting (RR = 0.94; 95% CI: 0.70-1.26; P = 0.69), moderate stunting (RR = 0.95; 95% CI: 0.76-1.19; P = 0.67) and mortality (RR = 0.83; 95% CI: 0.41-1.65; P = 0.59). Compared with LNS-LQ, LNS-MQ showed a greater protective effect on moderate acute malnutrition among children with good dietary adequacy: RR = 0.72; 95% CI: 0.56-0.94; P = 0.01. These results highlight the need to design context-specific programmes. Provision of LNS-LQ might be more appropriate when food insecurity is high, while when food security is better, distribution of LNS-MQ might be more appropriate.
Keywords: Niger; cash transfer; lipid-based nutrient supplement; prevention; stunting; undernutrition.
© 2016 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflict of interest. None of the authors received specific salary support from the funders for this project and publication.
Figures
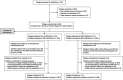
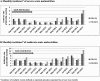
References
-
- Adu‐Afarwuah S., Lartey A., Brown K.H., Zlotkin S., Briend A. & Dewey K.G. (2007) Randomized comparison of 3 types of micronutrient supplements for home fortification of complementary foods in Ghana: effects on growth and motor development. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 86, 412–420. - PubMed
-
- Ackatia‐Armah R.S., McDonald C.M., Doumbia S., Erhardt J.G., Hamer D.H. & Brown K.H. (2015) Malian children with moderate acute malnutrition who are treated with lipid‐based dietary supplements have greater weight gains and recovery rates than those treated with locally produced cereal‐legume products: a community‐based, cluster randomized trial. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 101 (3), 632–645. - PubMed
-
- Black E.R., Victora C.G., Walker S.P., Bhutta Z.A., Christian P., de Onis M. et al. (2013) Maternal and child undernutrition and overweight in low‐income and middle‐income countries. Lancet 382, 427–435. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

