Regulated necrosis: disease relevance and therapeutic opportunities
- PMID: 26775689
- PMCID: PMC6531857
- DOI: 10.1038/nrd.2015.6
Regulated necrosis: disease relevance and therapeutic opportunities
Abstract
The discovery of regulated cell death presents tantalizing possibilities for gaining control over the life-death decisions made by cells in disease. Although apoptosis has been the focus of drug discovery for many years, recent research has identified regulatory mechanisms and signalling pathways for previously unrecognized, regulated necrotic cell death routines. Distinct critical nodes have been characterized for some of these alternative cell death routines, whereas other cell death routines are just beginning to be unravelled. In this Review, we describe forms of regulated necrotic cell death, including necroptosis, the emerging cell death modality of ferroptosis (and the related oxytosis) and the less well comprehended parthanatos and cyclophilin D-mediated necrosis. We focus on small molecules, proteins and pathways that can induce and inhibit these non-apoptotic forms of cell death, and discuss strategies for translating this understanding into new therapeutics for certain disease contexts.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement
The authors declare
Figures
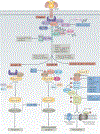

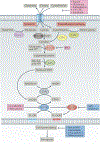
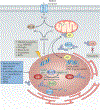
References
-
- Laster SM, Wood JG & Gooding LR Tumor necrosis factor can induce both apoptic and necrotic forms of cell lysis. J. Immunol 141, 2629–2634 (1988). - PubMed
-
- Vanden Berghe T, Linkermann A, Jouan-Lanhouet S, Walczak H & Vandenabeele P Regulated necrosis: the expanding network of non-apoptotic cell death pathways. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 15, 135–147 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

