TLR2 and TLR4 mediated host immune responses in major infectious diseases: a review
- PMID: 26775799
- PMCID: PMC9427569
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bjid.2015.10.011
TLR2 and TLR4 mediated host immune responses in major infectious diseases: a review
Abstract
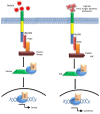
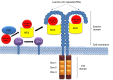
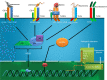
During the course of evolution, multicellular organisms have been orchestrated with an efficient and versatile immune system to counteract diverse group of pathogenic organisms. Pathogen recognition is considered as the most critical step behind eliciting adequate immune response during an infection. Hitherto Toll-like receptors (TLRs), especially the surface ones viz. TLR2 and TLR4 have gained immense importance due to their extreme ability of identifying distinct molecular patterns from invading pathogens. These pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) not only act as innate sensor but also shape and bridge innate and adaptive immune responses. In addition, they also play a pivotal role in regulating the balance between Th1 and Th2 type of response essential for the survivability of the host. In this work, major achievements rather findings made on the typical signalling and immunopathological attributes of TLR2 and TLR4 mediated host response against the major infectious diseases have been reviewed. Infectious diseases like tuberculosis, trypanosomiasis, malaria, and filariasis are still posing myriad threat to mankind. Furthermore, increasing resistance of the causative organisms against available therapeutics is also an emerging problem. Thus, stimulation of host immune response with TLR2 and TLR4 agonist can be the option of choice to treat such diseases in future.
Keywords: Filariasis; Malaria; Toll like receptor (TLR); Trypanosomiasis.
Copyright © 2016. Published by Elsevier Editora Ltda.
Figures


References
-
- Kawai T., Akira S. Toll-like receptors and their crosstalk with other innate receptors in infection and immunity. Immunity. 2011;34:637–650. - PubMed
-
- Zeytun A., Chaudhary A., Pardington P., Cary R., Gupta G. Induction of cytokines and chemokines by Toll-like receptor signaling strategies for control of inflammation. Crit Rev Immunol. 2010;30:53–67. - PubMed
-
- Valanne S., Wang J.H., Ramet M. The Drosophila Toll signaling pathway. J Immunol. 2011;186:649–656. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

