Anisotropic Effects on the Thermoelectric Properties of Highly Oriented Electrodeposited Bi2Te3 Films
- PMID: 26776726
- PMCID: PMC4726026
- DOI: 10.1038/srep19129
Anisotropic Effects on the Thermoelectric Properties of Highly Oriented Electrodeposited Bi2Te3 Films
Abstract
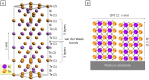
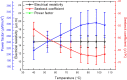
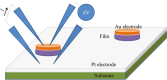
Highly oriented [1 1 0] Bi2Te3 films were obtained by pulsed electrodeposition. The structure, composition, and morphology of these films were characterized. The thermoelectric figure of merit (zT), both parallel and perpendicular to the substrate surface, were determined by measuring the Seebeck coefficient, electrical conductivity, and thermal conductivity in each direction. At 300 K, the in-plane and out-of-plane figure of merits of these Bi2Te3 films were (5.6 ± 1.2)·10(-2) and (10.4 ± 2.6)·10(-2), respectively.
Figures



References
-
- Martín-González M. et al.. Nanoengineering thermoelectrics for 21st century: Energy harvesting and other trends in the field. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 24, 288–305 (2013).
-
- Snyder G. J. et al.. Complex thermoelectric materials. Nat Mater 7, 105–114 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Greenaway D. L. et al.. Band structure of bismuth telluride, bismuth selenide and their respective alloys. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids 26, 1585–1604 (1965).
-
- Delves R. T. et al.. Anisotropy of the Electrical Conductivity in Bismuth Telluride. Proceedings of the Physical Society 78, 838 (1961).
-
- Goldsmid H. J. Recent Studies of Bismuth Telluride and Its Alloys. Journal of Applied Physics 32, 2198–2202 (1961).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

