Inhibiting the immunoproteasome exacerbates the pathogenesis of systemic Candida albicans infection in mice
- PMID: 26776888
- PMCID: PMC4726078
- DOI: 10.1038/srep19434
Inhibiting the immunoproteasome exacerbates the pathogenesis of systemic Candida albicans infection in mice
Abstract
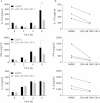
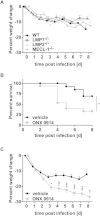
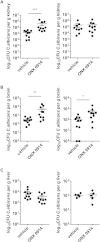
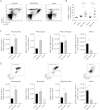
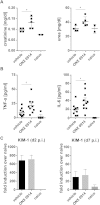
Apart from its role in MHC class I antigen processing, the immunoproteasome has recently been implicated in the modulation of T helper cell differentiation under polarizing conditions in vitro and in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases in vivo. In this study, we investigated the influence of LMP7 on T helper cell differentiation in response to the fungus Candida albicans. We observed a strong effect of ONX 0914, an LMP7-selective inhibitor of the immunoproteasome, on IFN-γ and IL-17A production by murine splenocytes and human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) stimulated with C. albicans in vitro. Using a murine model of systemic candidiasis, we could confirm reduced generation of IFN-γ- and IL-17A-producing cells in ONX 0914 treated mice in vivo. Interestingly, ONX 0914 treatment resulted in increased susceptibility to systemic candidiasis, which manifested at very early stages of infection. Mice treated with ONX 0914 showed markedly increased kidney and brain fungal burden which resulted in enhanced neutrophil recruitment and immunopathology. Together, these results strongly suggest a role of the immunoproteasome in promoting proinflammatory T helper cells in response to C. albicans but also in affecting the innate antifungal immunity in a T helper cell-independent manner.
Figures



References
-
- Goldberg A. L. & Rock K. L. Proteolysis, proteasomes and antigen presentation. Nature 357, 375–379 (1992). - PubMed
-
- Coux O., Tanaka K. & Goldberg A. L. Structure and functions of the 20S and 26S proteasomes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 65, 801–847 (1996). - PubMed
-
- Rock K. L. et al.. Inhibitors of the proteasome block the degradation of most cell proteins and the generation of peptides presented on MHC class I molecules. Cell 78, 761–771 (1994). - PubMed
-
- Groettrup M., Khan S., Schwarz K. & Schmidtke G. Interferon-gamma inducible exchanges of 20S proteasome active site subunits: why? Biochimie 83, 367–372 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Barton L. F., Cruz M., Rangwala R., Deepe G. S. & Monaco J. J. Regulation of immunoproteasome subunit expression in vivo following pathogenic fungal infection. J. Immunol. 169, 3046–3052 (2002). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

