Arkypallidal Cells Send a Stop Signal to Striatum
- PMID: 26777273
- PMCID: PMC4871723
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.12.017
Arkypallidal Cells Send a Stop Signal to Striatum
Abstract
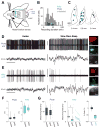
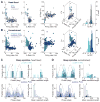
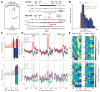
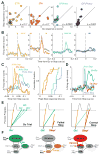
The suppression of inappropriate actions is critical for flexible behavior. Cortical-basal ganglia networks provide key gating mechanisms for action suppression, yet the specific roles of neuronal subpopulations are poorly understood. Here, we examine Arkypallidal (‘‘Arky’’) and Prototypical (‘‘Proto’’) globus pallidus neurons during a Stop task, which requires abrupt cancellation of an imminent action. We first establish that Arky neurons can be identified by their firing properties across the natural sleep/wake cycle. We then show that Stop responses are earlier and stronger in the Arky compared to the Proto subpopulation. In contrast to other basal ganglia neurons, pallidal Stop responses are selective to Stop, rather than Go, cues. Furthermore, the timing of these Stop responses matches the suppression of developing striatal Go-related activity. Our results support a two-step model of action suppression: actions-inpreparation are first paused via a subthalamic-nigral pathway, then cancelled via Arky GABAergic projections to striatum.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Stop and Think about Basal Ganglia Functional Organization: The Pallido-Striatal "Stop" Route.Neuron. 2016 Jan 20;89(2):237-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.01.003. Neuron. 2016. PMID: 26796685
-
A STOP signal to striatum mediated by globus pallidus: A new loop discovered.Mov Disord. 2016 Aug;31(8):1142. doi: 10.1002/mds.26648. Epub 2016 Apr 19. Mov Disord. 2016. PMID: 27089855 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bari A, Robbins TW. Inhibition and impulsivity: behavioral and neural basis of response control. Prog Neurobiol. 2013;108:44–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

