Global nitrogen budgets in cereals: A 50-year assessment for maize, rice, and wheat production systems
- PMID: 26778035
- PMCID: PMC4726071
- DOI: 10.1038/srep19355
Global nitrogen budgets in cereals: A 50-year assessment for maize, rice, and wheat production systems
Abstract
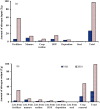
Industrially produced N-fertilizer is essential to the production of cereals that supports current and projected human populations. We constructed a top-down global N budget for maize, rice, and wheat for a 50-year period (1961 to 2010). Cereals harvested a total of 1551 Tg of N, of which 48% was supplied through fertilizer-N and 4% came from net soil depletion. An estimated 48% (737 Tg) of crop N, equal to 29, 38, and 25 kg ha(-1) yr(-1) for maize, rice, and wheat, respectively, is contributed by sources other than fertilizer- or soil-N. Non-symbiotic N2 fixation appears to be the major source of this N, which is 370 Tg or 24% of total N in the crop, corresponding to 13, 22, and 13 kg ha(-1) yr(-1) for maize, rice, and wheat, respectively. Manure (217 Tg or 14%) and atmospheric deposition (96 Tg or 6%) are the other sources of N. Crop residues and seed contribute marginally. Our scaling-down approach to estimate the contribution of non-symbiotic N2 fixation is robust because it focuses on global quantities of N in sources and sinks that are easier to estimate, in contrast to estimating N losses per se, because losses are highly soil-, climate-, and crop-specific.
Figures



References
-
- Galloway J. N. et al. Nitrogen cycles: past, present, and future. Biogeochem. 70, 153–226 (2004).
-
- Fowler D. et al. The global nitrogen cycle in the twenty-first century. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 368, 20130164 (2013) Available at: http://dx.doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2013.0134. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Connor D. J. Organic agriculture cannot feed the world. Field Crops Res. 106, 187–190 (2008).
-
- Dobermann A. & Cassman K. G. Cereal area and nitrogen use efficiency are drivers of future nitrogen fertilizer consumption. Science in China Ser. C: Life Sci. 48, 745–758 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Mueller N. D. et al. A tradeoff frontier for global nitrogen use and cereal production. Environ. Res. Lett. 9, 054002 (8pp) (2014).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

