Ivermectin versus albendazole or thiabendazole for Strongyloides stercoralis infection
- PMID: 26778150
- PMCID: PMC4916931
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD007745.pub3
Ivermectin versus albendazole or thiabendazole for Strongyloides stercoralis infection
Abstract
Background: Strongyloidiasis is a gut infection with Strongyloides stercoralis which is common world wide. Chronic infection usually causes a skin rash, vomiting, diarrhoea or constipation, and respiratory problems, and it can be fatal in people with immune deficiency. It may be treated with ivermectin or albendazole or thiabendazole.
Objectives: To assess the effects of ivermectin versus benzimidazoles (albendazole and thiabendazole) for treating chronic strongyloides infection.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Infectious Diseases Group Specialized Register (24 August 2015); the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), published in the Cochrane Library; MEDLINE (January 1966 to August 2015); EMBASE (January 1980 to August 2015); LILACS (August 2015); and reference lists of articles. We also searched the metaRegister of Controlled Trials (mRCT) using 'strongyloid*' as a search term, reference lists, and conference abstracts.
Selection criteria: Randomized controlled trials of ivermectin versus albendazole or thiabendazole for treating chronic strongyloides infection.
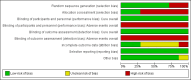
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently extracted data and assessed risk of bias in the included trials. We used risk ratios (RRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) and fixed- or random-effects models. We pooled adverse event data if the trials were sufficiently similar in their adverse event definitions.
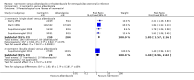
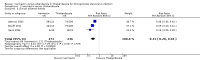
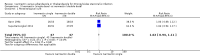
Main results: We included seven trials, enrolling 1147 participants, conducted between 1994 and 2011 in different locations (Africa, Southeast Asia, America and Europe).In trials comparing ivermectin with albendazole, parasitological cure was higher with ivermectin (RR 1.79, 95% CI 1.55 to 2.08; 478 participants, four trials, moderate quality evidence). There were no statistically significant differences in adverse events (RR 0.80, 95% CI 0.59 to 1.09; 518 participants, four trials, low quality evidence).In trials comparing ivermectin with thiabendazole, there was little or no difference in parasitological cure (RR 1.07, 95% CI 0.96 to 1.20; 467 participants, three trials, low quality evidence). However, adverse events were less common with ivermectin (RR 0.31, 95% CI 0.20 to 0.50; 507 participants; three trials, moderate quality evidence).In trials comparing different dosages of ivermectin, taking a second dose of 200 μg/kg of ivermectin was not associated with higher cure in a small subgroup of participants (RR 1.02, 95% CI 0.94 to 1.11; 94 participants, two trials).Dizziness, nausea, and disorientation were commonly reported in all drug groups. There were no reports of serious adverse events or death.
Authors' conclusions: Ivermectin results in more people cured than albendazole, and is at least as well tolerated. In trials of ivermectin with thiabendazole, parasitological cure is similar but there are more adverse events with thiabendazole.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflicts of interest.
Figures













Comment in
-
Treatment for chronic Strongyloides stercoralis infection: moderate-to-low evidence shows that ivermectin is more effective and tolerable than albendazole and thiabendazole, respectively.Evid Based Med. 2016 Jun;21(3):102. doi: 10.1136/ebmed-2016-110417. Epub 2016 Apr 25. Evid Based Med. 2016. PMID: 27112446 No abstract available.
References
References to studies included in this review
Adenusi 2003 {published data only}
-
- Adenusi A, Oke A, Adenusi O. Comparison of ivermectin and thiabendazole in the treatment of uncomplicated human Strongyloides stercoralis infection. African Journal of Biotechnology 2003;2(11):466‐9.
Bisoffi 2011 {published and unpublished data}
Datry 1994 {published data only}
-
- Datry A, Hilmarsdottir I, Mayorga‐Sagastume R, Lyagoubi M, Gaxotte P, Biligui S, et al. Treatment of Strongyloides stercoralis infection with ivermectin compared with albendazole: results of an open study of 60 cases. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1994;88(3):344‐5. - PubMed
Gann 1994 {published data only}
-
- Gann PH, Neva FA, Gam AA. A randomized trial of single‐ and two‐dose ivermectin versus thiabendazole for treatment of strongyloidiasis. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1994;169(5):1076‐9. - PubMed
Marti 1996 {published data only}
-
- Marti H, Haji H, Savioli L, Chwaya H, Mgeni A, Ameir J, et al. A comparative trial of a single‐dose Ivermectin versus three days of Albendazole for treatment of Strongyloides stercoralis and other soil‐transmitted helminth infections in children. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1996;55(5):477‐81. - PubMed
Suputtamongkol 2008 {published data only}
-
- Suputtamongkol Y, Kungpanichkul N, Silpasakorn S, Beeching N. Efficacy and safety of a single‐dose veterinary preparation of ivermectin versus 7‐day high‐dose albendazole for chronic strongyloidiasis. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents 2008;31(1):46‐9. - PubMed
Suputtamongkol 2011 {published data only}
References to studies excluded from this review
Archibald 1993 {published data only}
-
- Archibald L, Beeching N, Gill G, Bailey J, Bell D. Albendazole is effective treatment for chronic strongyloidiasis. Quarterly Journal of Medicine 1993;86(3):191‐5. - PubMed
Beus 1989 {published data only}
-
- Beus A. A comparative study of thiabendazole and mebendazole in strongyloidiasis [Poredbeno ispitivanje tiabendazola i mebendazola u strongiloidozi [Croatian]]. Liječnički Vjesnik 1989;111(3):98‐101. - PubMed
Bezjak 1968 {published data only}
-
- Bezjak B. A clinical trial of thiabendazole in strongyloidiasis. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1968;17(5):733‐6. - PubMed
Chanthavanich 1989 {published data only}
-
- Chanthavanich P, Nontasut P, Prarinyanuprp V, Sa‐Nguankiat S. Repeated doses of albendazole against strongyloidiasis in Thai children. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health 1989;20(2):221‐6. - PubMed
Chaun 1967 {published data only}
-
- Chaun H. The treatment of chronic strongyloidiasis with thiabendazole. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1967;61(6):812‐6. - PubMed
Franz 1963 {published data only}
-
- Franz K. Clinical trials with thiabendazole against human strongyloidiasis. American Journal Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1963;14:211‐4. - PubMed
Grove 1982 {published data only}
-
- Grove DI. Treatment of strongyloidiasis with thiabendazole: an analysis of toxicity and effectiveness. Transaction of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1982;76(1):114‐8. - PubMed
Gupte 1975 {published data only}
-
- Gupte S. Treatment of strongyloidiasis. Indian Pediatrics 1975;12(7):611. - PubMed
Huapaya 2003 {published data only}
-
- Huapaya P, Epinoza Y, Huiza A, Sevilla C, Vildósola H. Treatment of Strongyloides stercoralis with ivermectin and thiabendazole [Tratamiento de Strongylodes stercoralis con ivermectina y tiabendazole]. Anales de la Facultad de Medicina 2003;64(2):89‐93.
Igual‐Adell 2004 {published data only}
-
- Igual‐Adell R, Oltra‐Alcaraz C, Soler‐Company E, Sánchez‐Sánchez P, Matogo‐Oyana J, Rodríguez‐Calabuig D. Efficacy and safety of ivermectin and thiabendazole in the treatment of strongyloidiasis. Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy 2004;5(12):2615‐9. - PubMed
Krubwa 1974 {published data only}
-
- Krubwa F, Gatti F, Lontie M, Nguete K, Vandepitte J, Thienpont D. Quarterly administration of mebendazole to suburban school children [Administration trimestrielle de Mebendazole en milieu scolaire suburbain]. Medecine Tropicale 1974;34(5):679‐87.
Marcos 2005 {published data only}
-
- Marcos L, Terashima A, Samalvides F, Alvarez H, Lindo F, Tello R, et al. Thiabendazole for control of Strongyloides stercoralis infection in a hyperendemic area of Peru [Tiabendazol para el control de la infección por Strongyloides stercoralis en una zona hiperendémica en el Perú]. Revista Gastroenterología del Perú 2005;25(4):341‐8. - PubMed
Mojon 1987 {published data only}
-
- Mojon M, Nielsen PB. Treatment of Strongyloides stercoralis with albendazole. A cure rate of 86 per cent. Zentralblatt für Bakteriologie, Mikrobiologie, und Hygiene 1987;263(4):619‐24. - PubMed
Nampijja 2012 {published data only}
Naquira 1989 {published data only}
-
- Naquira C, Jimenez G, Guerra J, Bernal R, Nalin D, Neu D, et al. Ivermectin for human strongyloidiasis and other intestinal helminths. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1989;40(3):304‐9. - PubMed
Nimura 1992 {published data only}
-
- Nimura S, Hirata T, Zaha O, Nakamura H, Kouchi A, Uehara T, et al. Clinical study of albendazole therapy for strongyloidiasis [Japanese]. Kansenshōgaku Zasshi 1992;66(9):1231‐5. - PubMed
Nontasut 2005 {published data only}
-
- Nontasut P, Muennoo C, Sa‐nguankiat S, Fongsri S, Vichit A. Prevalence of strongyloides in northern Thailand and treatment with ivermectin vs albendazole. Southest Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health 2005;36(2):442‐4. - PubMed
Oyakawa 1991 {published data only}
-
- Oyakawa T, Kuniyoshi T. Arakaki T, Higashionna A, Shikiya K, Sakugawa H, et al. New trial with thiabendazole for treatment of human strongyloidiasis [Japanese]. Kansenshōgaku Zasshi 1991;65(3):304‐10. - PubMed
Pitisuttithum 1995 {published data only}
-
- Pitisuttithum P, Supanaranond W, Chindanond D. A randomized comparative study of albendazole and thiabendazole in chronic strongyloidiasis. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health 1995;26(4):735‐8. - PubMed
Portugal 2002 {published data only}
-
- Portugal R, Schaffel R, Almeida L, Spector N, Nucci M. Thiabendazole for the prophylaxis of strongyloidiasis in immunosuppressed patients with hematologic diseases: a randomized, double‐blind placebo‐controlled study. Haematologica 2002;87(6):663‐4. - PubMed
Pungpak 1987 {published data only}
-
- Pungpak S, Bunnag D, Chindanond D, Radmoyos B. Albendazoles in the treatment of strongyloidiasis. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health 1987;18(2):207‐10. - PubMed
Reynoldson 1997 {published data only}
-
- Reynoldson J, Behnke J, Pallant L, Macnish M, Gilbert F, Giles S, et al. Failure of pyrantel in treatment of human hookworm infections (Ancylostoma duodenale) in the Kimberley region of north west Australia. Acta Tropica 1997;68(3):301‐12. - PubMed
Rossignol 1983 {published data only}
-
- Rossignol JF, Maisonneuve H. Albendazole: placebo‐controlled study in 870 patients with intestinal helminthiasis. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1983;77(5):707‐11. - PubMed
Salazar 1994 {published data only}
-
- Salazar S, Berk S, Howe D, Berk S. Ivermectin vs thiabendazole in the treatment of strongyloidiasis. Infections in Medicine 1994;11(1):50‐9.
Schaffel 2000 {published data only}
-
- Schaffel R, Nucci M, Portugal R, Castro M, Ferrerira S, Almeida L, et al. Thiabendazole for the treatment of strongyloidiasis in patients with hematologic malignancies. Clinical of Infectious Diseases 2000;31(3):821‐2. - PubMed
Shikiya 1990 {published data only}
-
- Shikiya K, Kuniyoshu T, Higashionna A, Arakaki T, Oyakawa T, Kadena K, et al. Treatment of strongyloidiasis with mebendazole and its combination with thiabendazole [Japanese]. Kansenshōgaku Zasshi 1990;64(11):1408‐15. - PubMed
Shikiya 1991 {published data only}
-
- Shikiya K, Kinjo N, Ikema M, Yamashiro A, Uechi H, Oyakawa T, et al. Comparison of efficacy of powder and tablet of mebendazole in the treatment of strongyloidiasis. Kansenshōgaku Zasshi 1991;65(6):681‐6. - PubMed
Shikiya 1992 {published data only}
-
- Shikiya K, Zaha O, Niimura S, Nakamura H, Nakayoshi T, Kochi A, et al. Clinical study of eradicated and resistant patients to treatment with ivermectin for strongyloidiasis [Japanese]. Kansenshōgaku Zasshi 1992;66(7):935‐43. - PubMed
Shikiya 1994 {published data only}
-
- Shikiya K, Zaha O, Niimura S, Uehara T, Ohshiro J, Kinjo F, et al. Clinical study on ivermectin against 125 strongyloidiasis patients [Japanese]. Kansenshōgaku Zasshi 1994;68(1):13‐20. - PubMed
Singthong 2006 {published data only}
-
- Singthong S, Intapan P, Wongsaroji T, Maleewong W. Randomized comparative trial of two high‐dose albendazole regimens for uncomplicated human strongyloidiasis. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health 2006;37(Suppl 3):32‐4. - PubMed
Steinmann 2008 {published data only}
Toma 2000 {published data only}
-
- Toma H, Sato Y, Shiroma Y, Kobayashi J, Shimabukuro I, Takara M. Comparative studies on the efficacy of three anthelminthics on treatment of human strongyloidiasis in Okinawa, Japan. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health 2000;31(1):147‐51. - PubMed
Whitworth 1991 {published data only}
-
- Whitworth JA, Morgan D, Maude GH, McNicholas AM, Taylor DW. A field study of the effect of ivermectin on intestinal helminths in man. Transaction Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1991;85(2):232‐4. - PubMed
Xiao 2013 {published data only}
-
- Xiao SH, Utzinger J, Tanner M, Keiser J, Xue J. Advances with the Chinese anthelminthic drug tribendimidine in clinical trials and laboratory investigations. Acta Tropical 2013;126(2):115‐26. - PubMed
Yap 2013 {published data only}
Zaha 2004 {published data only}
-
- Zaha O, Hirata T, Uchima N, Kinjo F, Saito A. Comparison of anthelmintic effects of two doses of ivermectin on intestinal strongyloidiasis in patients negative or positive for anti‐HTLV‐1 antibody. Journal of Infection and Chemotherapy 2004;10(6):348‐51. - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
NCT01570504 {published data only}
-
- NCT01570504. Multiple Versus Single Dose of Ivermectin for the Treatment of Strongyloidiasis (STRONGTREAT). https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01570504 (accessed 24 August 2015). [NCT01570504]
Additional references
Angheben 2011
-
- Angheben A, Mistretta M, Gobbo M, Bonafini S, Lacovazzi T, Sepe A, et al. Acute strongyloidiasis in Italian tourists returning from Southeast Asia. Journal of Travel Medicine 2011;18(2):138‐40. - PubMed
Berk 1987
-
- Berk S, Verghese A, Alvarez S, Hall K, Smith B. Clinical and epidemiologic features of strongyloidiasis. A prospective study in rural Tennessee. Archives of Internal Medicine 1987;147(7):1257‐61. - PubMed
Bethony 2006
-
- Bethony J, Brooker S, Albonico M, Geiger SM, Loukas A, Diemert D, et al. Soil‐transmitted helminth infections: ascariasis, trichuriasis, and hookworm. Lancet 2006;367(9521):1521‐32. - PubMed
Bisoffi 2013
Bisoffi 2014
Boken 1993
-
- Boken DJ, Leoni PA, Preheim LC. Treatment of Strongyloides stercoralis hyperinfection syndrome with thiabendazole administered per rectum. Clinical Infectious Diseases 1993;16(1):123‐6. - PubMed
Buonfrate 2012
-
- Buonfrate D, Angheben A, Gobbi F, Munoz J, Requena‐Mendez A, Gotuzzo E, et al. Imported strongyloidiasis: epidemiology, presentations, and treatment. Current Infectious Disease Reports 2012;14(3):256‐62. - PubMed
Buonfrate 2013
Campbell 1991
-
- Campbell WC. Ivermectin as an anti parasitic agent for use in humans. Annual Review of Microbiology 1991;45:445‐74. - PubMed
CDC 2013
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Strongyloides. http://www.cdc.gov/parasites/strongyloides/health_professionals/ (accessed 24 August 2015).
Cook 1992
-
- Cook GC. Use of antiprotozoan and anthelmintic drugs during pregnancy: side‐effects and contra‐indications. Journal of Infection 1992;25(1):1‐9. - PubMed
Coovadia 1993
-
- Coovadia YM, Rajput MC, Bhana RH. Disseminated strongyloidiasis in a diabetic patient. Tropical and Geographical Medicine 1993;45(4):179‐80. - PubMed
Courouble 2004
-
- Courouble G, Rouet F, Herrmann‐Storck C, Nicolas M, Candolfi E, Deloumeaux J, et al. Epidemiologic study of the association between human T‐cell lymphotropic virus type 1 and Strongyloides stercoralis infection in female blood donors (Guadeloupe, French West Indies). West Indian Medical Journal 2004;53(1):3‐6. - PubMed
Crump 2011
dos Santos 2009
-
- dos Santos AR, Falcão CA, Muzitano MF, Kaiser CR, Rossi‐Bergmann B, Férézou J. Ivermectin‐derived leishmanicidal compounds. Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry 2009;17(2):496‐502. - PubMed
Fardet 2007
-
- Fardet L, Généreau T, Poirot JL, Guidet B, Kettaneh A, Cabane J. Severe strongyloidiasis in corticosteroid treated patients: case series and literature review. Journal of Infection 2007;54(1):18‐27. - PubMed
Freedman 1991
-
- Freedman D. Experimental infection of human subjects with Strongyloides species. Reviews of Infectious Diseases 1991;13(6):1221‐6. - PubMed
Geary 2005
-
- Geary TG. Ivermectin 20 years on: maturation of a wonder drug. Trends in Parasitology 2005;21(11):530‐2. - PubMed
Heukelbach 2004
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC (editors). Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Hirata 2006
-
- Hirata T, Uchima N, Kishimoto K, Zaha O, Kinjo N, Hokama A, et al. Impairment of host immune response against Strongyloides stercoralis by human T cell lymphotropic virus type 1 infection. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2006;74(2):246‐9. - PubMed
Horton 2000
-
- Horton J. Albendazole: a review of anthelmintic efficacy and safety in humans. Parasitology 2000;121(Suppl):S113‐32. - PubMed
Keiser 2004
Lacey 1990
-
- Lacey E. Mode of action of benzimidazoles. Parasitology Today 1990;6(4):112‐5. - PubMed
Lefebvre 2011
-
- Lefebvre C, Manheimer E, Glanville J. Chapter 6: Searching for studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.1 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Liu 1996
-
- Liu LX, Weller PF. Antiparasitic drugs. New England Journal of Medicine 1996;334(18):1178‐84. - PubMed
Maguire 2005
-
- Maguire J. Intestinal nematodes. In: Mandell GL, Bennett JE, Dolin R editor(s). Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 6th Edition. Vol. 2, Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2005:3260‐7.
Marty 2005
-
- Marty FM, Lowry CM, Rodriguez M, Milner DA, Pieciak WS, Sinha A, et al. Treatment of human disseminated strongyloidiasis with a parenteral veterinary formulation of ivermectin. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2005;41(1):e5‐8. - PubMed
Mejia 2012
Merck 2007
-
- Merck, Co. Inc. Tablets: Stromectol® (ivermectin) [NDA 50‐742/S‐022]. 2007. www.fda.gov/medwatch/safety/2008/Sep_PI/Stromectol_PI.pdf (accessed February 2009).
Miller 2008
-
- Miller MA, Church LW, Salgado CD. Strongyloides hyperinfection: a treatment dilemma. American Journal of the Medical Sciences 2008;336(4):358‐61. - PubMed
Moncayo 2008
Montes 2010
Nahmias 1994
-
- Nahmias J, Goldsmith R, Soibelman M, el‐On J. Three‐ to 7‐year follow‐up after albendazole treatment of 68 patients with cystic echinococcosis (hydatid disease). Annals of Tropical Medicine and Parasitology 1994;88(3):295‐304. - PubMed
Nucci 1995
-
- Nucci M, Portugal R, Pulcheri W, Spector N, Ferreira SB, Castro M, et al. Strongyloidiasis in patients with hematologic malignancies. Clinical Infectious Diseases 1995;21(3):675‐7. - PubMed
Nuesch 2005
-
- Nuesch R, Zimmerli L, Stockli R, Gyr N, Christoph Hatz FR. Imported strongyloidosis: a longitudinal analysis of 31 cases. Journal of Travel Medicine 2005;12(2):80‐4. - PubMed
Olsen 2009
-
- Olsen A, Lieshout L, Marti H, Polderman T, Polman K, Steinmann P, et al. Strongyloidiasis‐the most neglected of the neglected tropical diseases?. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2009;103(10):967‐72. - PubMed
Ottesen 1994
-
- Ottesen EA, Campbell WC. Ivermectin in human medicine. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1994;34(2):195‐203. - PubMed
Ottesen 2008
Pacanowski 2005
-
- Pacanowski J, Santos MD, Roux A, Maignan C, Guillot J, Lavarde V, et al. Subcutaneous ivermectin as a safe salvage therapy in Strongyloides stercoralis hyperinfection syndrome: a case report. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2005;73(1):122‐4. - PubMed
Patel 2008
-
- Patel G, Arvelakis A, Sauter BV, Gondolesi GE, Caplivski D, Huprikar S. Strongyloides hyperinfection syndrome after intestinal transplantation. Transplant Infectious Disease 2008;10(2):137‐41. - PubMed
Ramanathan 2008
Requena‐Méndez 2013
Review Manager (RevMan) [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Salluh 2005
-
- Salluh JI, Feres GA, Velasco E, Holanda GS, Toscano L, Soares M. Successful use of parenteral ivermectin in an immunosuppressed patient with disseminated strongyloidiasis and septic shock. Intensive Care Medicine 2005;31(9):1292. - PubMed
Santiago 2009
-
- Santiago M, Leitão B. Prevention of strongyloides hyperinfection syndrome: a rheumatological point of view. European Journal of Internal Medicine 2009;20(8):744‐8. - PubMed
Schär 2013
Streit 2008
-
- Streit A. Reproduction in Strongyloides (Nematoda): a life between sex and parthenogenesis. Parasitology 2008;135(3):285‐94. - PubMed
Tarr 2003
-
- Tarr PE, Miele PS, Peregoy KS, Smith MA, Neva FA, Lucey DR. Case report: Rectal administration of ivermectin to a patient with Strongyloides hyperinfection syndrome. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2003;68(4):453‐5. - PubMed
Ten Hove 2009
The Medical Letter 2013
-
- The Medical Letter. Drugs for parasitic infections. The Medical Letter. 3rd Edition. New York: The Medical Letter Inc., 2013:e20.
Traore 2012
van Doorn 2007
Walzer 1982
-
- Walzer PD, Milder JE, Banwell JG, Kilgore G, Klein M, Parker R. Epidemiologic features of Strongyloides stercoralis infection in an endemic area of the United States. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1982;31(2):313‐9. - PubMed
WHO 2006
-
- World Health Organization. Preventive chemotherapy in human helminthiasis: coordinated use of anthelminthic drugs in control interventions: a manual for health professionals and programme managers. Geneva: WHO, 2006.
WHO 2015
-
- World Health Organization. Model List of Essential Medicines. 19th List. Essential medicines and health products April 2015.
Yori 2006
Zago‐Gomes 2002
-
- Zago‐Gomes MP, Aikawa KF, Perazzio SF, Gonçalves CS, Pereira FE. Prevalence of intestinal nematodes in alcoholic patients. Revista da Sociedade Brasileira de Medicina Tropical 2002;35(6):571‐4. - PubMed
Zaha 2000
-
- Zaha O, Hirata T, Kinjo F, Saito A. Strongyloidiasis‐‐progress in diagnosis and treatment. Internal Medicine 2000;39(9):695‐700. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Henriquez‐Camacho 2012
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

