In Vitro Model of the Epidermis: Connecting Protein Function to 3D Structure
- PMID: 26778564
- PMCID: PMC4870045
- DOI: 10.1016/bs.mie.2015.07.015
In Vitro Model of the Epidermis: Connecting Protein Function to 3D Structure
Abstract
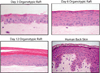
Much of our understanding of the biological processes that underlie cellular functions in humans, such as cell-cell communication, intracellular signaling, and transcriptional and posttranscriptional control of gene expression, has been acquired from studying cells in a two-dimensional (2D) tissue culture environment. However, it has become increasingly evident that the 2D environment does not support certain cell functions. The need for more physiologically relevant models prompted the development of three-dimensional (3D) cultures of epithelial, endothelial, and neuronal tissues (Shamir & Ewald, 2014). These models afford investigators with powerful tools to study the contribution of spatial organization, often in the context of relevant extracellular matrix and stromal components, to cellular and tissue homeostasis in normal and disease states.
Keywords: Desmoglein; Epidermis; Keratinocyte; Organotypic.
© 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Ader M, Tanaka EM. Modeling human development in 3D culture. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2014;31:23–28. - PubMed
-
- Asselineau D, Prunieras M. Reconstruction of 'simplified' skin: control of fabrication. Br J Dermatol. 1984;111(Suppl 27):219–222. - PubMed
-
- Barreca A, De Luca M, Del Monte P, Bondanza S, Damonte G, Cariola G, Di Marco E, Giordano G, Cancedda R, Minuto F. In vitro paracrine regulation of human keratinocyte growth by fibroblast-derived insulin-like growth factors. J Cell Physiol. 1992;151(2):262–268. - PubMed
-
- Bilousova G, Roop DR. Generation of functional multipotent keratinocytes from mouse induced pluripotent stem cells. Methods Mol Biol. 2013;961:337–350. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

