Prevalence of chronic kidney disease-mineral and bone disorder in incident peritoneal dialysis patients and its association with short-term outcomes
- PMID: 26778726
- PMCID: PMC5331134
- DOI: 10.11622/smedj.2015195
Prevalence of chronic kidney disease-mineral and bone disorder in incident peritoneal dialysis patients and its association with short-term outcomes
Abstract
Introduction: A complex relationship exists between chronic kidney disease-mineral and bone disorder (CKD-MBD) and adverse outcomes among dialysis patients. This study aimed to report the prevalence of CKD-MBD and examine the impact of achieving target CKD-MBD parameters on morbidity and mortality one year after peritoneal dialysis (PD) initiation.
Methods: In this retrospective cohort study, patients electively initiated on PD were followed up for one year. Laboratory parameters were collected and the prevalence of CKD-MBD 4-6 months after PD initiation was determined based on the Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (KDOQI) and Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) guidelines. Linear regression and Cox proportional hazards model were used to evaluate the effects of achieving CKD-MBD targets 4-6 months after PD initiation on hospitalisation, the incidence of peritonitis or exit-site infections (ESIs), and mortality at one year.
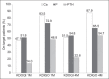
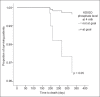
Results: The prevalence of CKD-MBD among the 86 patients in this study was 86.0% (KDOQI) and 54.7% (KDIGO). There was no significant difference in hospitalisation duration between patients who achieved targets and those who did not. Patients who failed to meet all the KDIGO CKD-MBD or calcium serum targets had a higher incidence of peritonitis or ESI. A trend toward shorter time to death was observed among patients who failed to meet the KDIGO phosphorus serum targets.
Conclusion: There was moderate (KDIGO) to high prevalence (KDOQI) of CKD-MBD among the patients. Achievement of all the KDIGO CKD-MBD or calcium serum targets was associated with reduced peritonitis or ESI, while achievement of the KDIGO phosphorus serum targets was associated with improved survival.
Keywords: incident; mineral and bone disorder; outcomes; peritoneal dialysis; short-term.
Copyright: © Singapore Medical Association
Figures


References
-
- Martin KJ, González EA. Metabolic bone disease in chronic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;18:875–85. - PubMed
-
- Raggi P, Kleerekoper M. Contribution of bone and mineral abnormalities to cardiovascular disease in patients with chronic kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008;3:836–43. - PubMed
-
- Noordzij M, Korevaar JC, Bos WJ, et al. Mineral metabolism and cardiovascular morbidity and mortality risk: peritoneal dialysis patients compared with haemodialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2006;21:2513–20. - PubMed
-
- Young EW, Albert JM, Satayathum S, et al. Predictors and consequences of altered mineral metabolism: the Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study. Kidney Int. 2005;67:1179–87. - PubMed
-
- Tentori F, Blayney MJ, Albert JM, et al. Mortality risk for dialysis patients with different levels of serum calcium, phosphorus, and PTH: the Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study (DOPPS) Am J Kidney Dis. 2008;52:519–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

