miRNA and cholesterol homeostasis
- PMID: 26778752
- PMCID: PMC4980302
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2016.01.005
miRNA and cholesterol homeostasis
Abstract
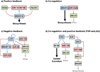
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have recently emerged as a novel class of epigenetic regulators of gene expression. They are systemically involved in the control of lipid metabolism through a complex interactive mechanism that involves gene regulatory networks. Hence, they can contribute to defective lipid metabolism and metabolic diseases. Here, we review recent advances in the roles of lipid-sensing transcription factors in regulating miRNA gene networks, as well as miRNA expression and function in the regulation of cholesterol metabolism. This article is part of a Special Issue entitled: MicroRNAs and lipid/energy metabolism and related diseases edited by Carlos Fernández-Hernando and Yajaira Suárez.
Keywords: Cholesterol metabolism; Metabolic disease; MicroRNA; Transcription factor.
Copyright © 2016. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
We have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Maxfield FR, Tabas I. Role of cholesterol and lipid organization in disease. Nature. 2005;438:612–621. - PubMed
-
- Luu W, Sharpe LJ, Gelissen IC, Brown AJ. The role of signalling in cellular cholesterol homeostasis. IUBMB Life. 2013;65:675–684. - PubMed
-
- Osborne TF. Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBPs): key regulators of nutritional homeostasis and insulin action. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:32379–32382. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

