Drug poisoning deaths in the United States, 1999-2012: a statistical adjustment analysis
- PMID: 26778921
- PMCID: PMC4714527
- DOI: 10.1186/s12963-016-0071-7
Drug poisoning deaths in the United States, 1999-2012: a statistical adjustment analysis
Abstract
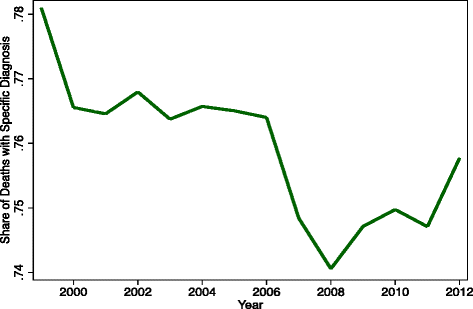
Background: Drug poisoning mortality in the US has risen rapidly but the drugs involved are frequently unspecified on death certificates.
Methods: Reported and adjusted proportions of specific drug types involved in fatal drug poisonings were calculated using vital statistics mortality data from 1999 to 2012. The adjusted proportions were those predicted to occur if at least one specific type of drug had been identified on the death certificates of all poisoning fatalities.
Results: Adjusted involvement rates of opioid analgesic mentions in 2012 were 54.3 % (95 % confidence interval [CI]: 53.6 %-55 %), 40.8 % higher than the reported 38.6 % rate. Adjusted rates for all narcotics, other narcotics, sedatives, or psychotropics, and multiple drug use were 81.5 % (95 % CI: 80.9 %-82.2 %), 38.4 % (95 % CI: 37.8 %-39 %), 30 % (95 % CI: 29.4 %-30.7 %), 26 % (95 % CI: 25.4 %-26.6 %) and 42.8 % (95 % CI: 42.1 %-43.5 %) in 2012, compared to reported proportions of 60.7, 27.9, 18.7, 18 and 26.9 %. The adjustments typically had similar or slightly smaller effects on the estimates in 1999, and larger impacts on subcategories of drug types such benzodiazepines and antipsychotic medications. Based on the adjusted proportions, 22,534, 15,933, 12,457, 10,798, and 17,670 drug deaths in 2012 were estimated to involve opioid analgesics, other narcotics, sedatives, psychotropic medications, and drug combinations, compared to death certificate reports of 16,007, 11,567, 7,754, 7,467, and 11,176.
Conclusions: Death certificates substantially understate the involvement of opioid analgesics, sedatives, psychotropics, and drug combinations in fatal drug poisonings. Adjustment procedures that account for cases where only unspecified drugs are reported on death certificates provide more accurate information.
Keywords: Death certificates; Drug involvement; Drug poisoning mortality; Fatal drug poisonings; Poisoning deaths.
Figures
References
-
- Warner M, Chen LH, Makuc DM, Anderson RN, Miniño AM. Drug poisoning deaths in the United States, 1980–2008. NCHS data brief, No. 81. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics; 2011. - PubMed
-
- Chen LH, Hedegaard H, Warner M. Drug-Poisoning deaths involving opioid analgesics: United States, 1999–2011. NCHS data brief, No. 166. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics.; 2014. - PubMed
-
- CDC Vital Signs: Overdoses of prescription opioid pain relievers - United States, 1999–2008. MMWR. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2011;60(43):1487–92. - PubMed
-
- CDC Vital Signs: Risk for overdose from methadone used for pain relief – United States, 1999–2010. MMWR. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2012;61(26):493–7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources