Wireless, Ultra-Low-Power Implantable Sensor for Chronic Bladder Pressure Monitoring
- PMID: 26778926
- PMCID: PMC4712728
- DOI: 10.1145/2180878.2180883
Wireless, Ultra-Low-Power Implantable Sensor for Chronic Bladder Pressure Monitoring
Abstract
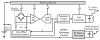
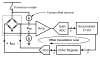
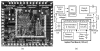
The wireless implantable/intracavity micromanometer (WIMM) system was designed to fulfill the unmet need for a chronic bladder pressure sensing device in urological fields such as urodynamics for diagnosis and neuromodulation for bladder control. Neuromodulation in particular would benefit from a wireless bladder pressure sensor which could provide real-time pressure feedback to an implanted stimulator, resulting in greater bladder capacity while using less power. The WIMM uses custom integrated circuitry, a MEMS transducer, and a wireless antenna to transmit pressure telemetry at a rate of 10 Hz. Aggressive power management techniques yield an average current draw of 9 μA from a 3.6-Volt micro-battery, which minimizes the implant size. Automatic pressure offset cancellation circuits maximize the sensing dynamic range to account for drifting pressure offset due to environmental factors, and a custom telemetry protocol allows transmission with minimum overhead. Wireless operation of the WIMM has demonstrated that the external receiver can receive the telemetry packets, and the low power consumption allows for at least 24 hours of operation with a 4-hour wireless recharge session.
Keywords: ASIC; Design; FSK transmitter; Measurement; ULP; bladder pressure; implant; low-power; neuromodulation; offset cancellation; urodynamics; wireless recharge; wireless sensor.
Figures
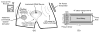





References
-
- Baker MW, Sarpeshkar R. Feedback analysis and design of RF power links for low-power bionic systems. IEEE Trans Biomed Circ Syst. 2007;1(1):28–38. - PubMed
-
- Chapple CR. Primer: Questionnaires versus urodynamics in the evaluation of lower urinary tract dysfunction-one, both or none? Nature Clinical Practice Urology. 2005;2:555–564. - PubMed
-
- Chow EY, Yang CL, Chlebowski A, Moon S, Chappel WJ, Irazoqui PP. Implantable wireless telemetry boards for in vivo transocular transmission. IEEE Trans Microwave Theory Techn. 2008;56(12):3200–3208.
-
- Cong P, Suster MA, Chaimanonart N, Young DJ. Wireless power recharging for implantable bladder pressure sensor. Proceedings of the 8th Annual IEEE Conference on Sensors; 2009. pp. 1670–1673.
-
- Cong P, Ko WH, Young DJ. Wireless batteryless implantable blood pressure monitoring microsystem for small laboratory animals. IEEE Sensors J. 2010;10(2):243–254.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
