Platelet Activating Factor Enhances Synaptic Vesicle Exocytosis Via PKC, Elevated Intracellular Calcium, and Modulation of Synapsin 1 Dynamics and Phosphorylation
- PMID: 26778968
- PMCID: PMC4705275
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2015.00505
Platelet Activating Factor Enhances Synaptic Vesicle Exocytosis Via PKC, Elevated Intracellular Calcium, and Modulation of Synapsin 1 Dynamics and Phosphorylation
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Platelet Activating Factor Enhances Synaptic Vesicle Exocytosis Via PKC, Elevated Intracellular Calcium, and Modulation of Synapsin 1 Dynamics and Phosphorylation.Front Cell Neurosci. 2016 May 4;10:113. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2016.00113. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27199666 Free PMC article.
Abstract
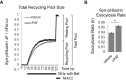
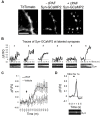
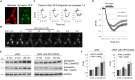
Platelet activating factor (PAF) is an inflammatory phospholipid signaling molecule implicated in synaptic plasticity, learning and memory and neurotoxicity during neuroinflammation. However, little is known about the intracellular mechanisms mediating PAF's physiological or pathological effects on synaptic facilitation. We show here that PAF receptors are localized at the synapse. Using fluorescent reporters of presynaptic activity we show that a non-hydrolysable analog of PAF (cPAF) enhances synaptic vesicle release from individual presynaptic boutons by increasing the size or release of the readily releasable pool and the exocytosis rate of the total recycling pool. cPAF also activates previously silent boutons resulting in vesicle release from a larger number of terminals. The underlying mechanism involves elevated calcium within presynaptic boutons and protein kinase C activation. Furthermore, cPAF increases synapsin I phosphorylation at sites 1 and 3, and increases dispersion of synapsin I from the presynaptic compartment during stimulation, freeing synaptic vesicles for subsequent release. These findings provide a conceptual framework for how PAF, regardless of its cellular origin, can modulate synapses during normal and pathologic synaptic activity.
Keywords: PAF; PKC; calcium; platelet activating factor; presynaptic plasticity; readily releasable pool; synapsin; synaptic vesicle pools.
Figures




Similar articles
-
[Presynaptic mechanisms of learning and memory].Brain Nerve. 2008 Jul;60(7):725-36. Brain Nerve. 2008. PMID: 18646612 Review. Japanese.
-
Dynamic Partitioning of Synaptic Vesicle Pools by the SNARE-Binding Protein Tomosyn.J Neurosci. 2016 Nov 2;36(44):11208-11222. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1297-16.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27807164 Free PMC article.
-
Corrigendum: Platelet Activating Factor Enhances Synaptic Vesicle Exocytosis Via PKC, Elevated Intracellular Calcium, and Modulation of Synapsin 1 Dynamics and Phosphorylation.Front Cell Neurosci. 2016 May 4;10:113. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2016.00113. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27199666 Free PMC article.
-
Apparent calcium dependence of vesicle recruitment.J Physiol. 2018 Oct;596(19):4693-4707. doi: 10.1113/JP275911. Epub 2018 Aug 7. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29928766 Free PMC article.
-
Synapsin regulation of vesicle organization and functional pools.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011 Jun;22(4):387-92. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2011.07.003. Epub 2011 Jul 31. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 21827866 Review.
Cited by
-
Serum Lipidome Change in Japanese Patients with Major Depressive Disorder: A Real-World Exploratory Study.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2025 Aug 21;21:1717-1729. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S541312. eCollection 2025. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2025. PMID: 40861884 Free PMC article.
-
Ginkgolide B improved postoperative cognitive dysfunction by inhibiting microgliosis-mediated neuroinflammation in the hippocampus of mice.BMC Anesthesiol. 2022 Jul 18;22(1):229. doi: 10.1186/s12871-022-01750-1. BMC Anesthesiol. 2022. PMID: 35850641 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering epigenetic landscape: a new path for biomarkers identification and drug development.Mol Biol Rep. 2020 Nov;47(11):9097-9122. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-05916-3. Epub 2020 Oct 21. Mol Biol Rep. 2020. PMID: 33089404 Review.
-
Transcriptomic Analysis of Mecp2 Mutant Mice Reveals Differentially Expressed Genes and Altered Mechanisms in Both Blood and Brain.Front Psychiatry. 2019 Apr 29;10:278. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00278. eCollection 2019. Front Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 31110484 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid and Gentle Immunopurification of Brain Synaptic Vesicles.J Neurosci. 2022 Apr 27;42(17):3512-3522. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2521-21.2022. Epub 2022 Mar 16. J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35296545 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akisu M., Huseyinov A., Yalaz M., Cetin H., Kultursay N. (2003). Selective head cooling with hypothermia suppresses the generation of platelet-activating factor in cerebrospinal fluid of newborn infants with perinatal asphyxia. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 69 45–50. 10.1016/S0952-3278(03)00055-3 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bazan N. G., Squinto S. P., Braquet P., Panetta T., Marcheselli V. L. (1991). Platelet-activating factor and polyunsaturated fatty acids in cerebral ischemia or convulsions: intracellular PAF-binding sites and activation of a fos/jun/AP-1 transcriptional signaling system. Lipids 26 1236–1242. 10.1007/BF02536539 - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

