Spectrally encoded confocal microscopy for diagnosing breast cancer in excision and margin specimens
- PMID: 26779830
- PMCID: PMC5027883
- DOI: 10.1038/labinvest.2015.158
Spectrally encoded confocal microscopy for diagnosing breast cancer in excision and margin specimens
Abstract
A large percentage of breast cancer patients treated with breast conserving surgery need to undergo multiple surgeries due to positive margins found during post-operative margin assessment. Carcinomas could be removed completely during the initial surgery and additional surgery avoided if positive margins can be determined intraoperatively. Spectrally encoded confocal microscopy (SECM) is a high-speed reflectance confocal microscopy technology that has a potential to rapidly image the entire surgical margin at subcellular resolution and accurately determine margin status intraoperatively. In this study, in order to test the feasibility of using SECM for intraoperative margin assessment, we have evaluated the diagnostic accuracy of SECM for detecting various types of breast cancers. Forty-six surgically removed breast specimens were imaged with an SECM system. Side-by-side comparison between SECM and histologic images showed that SECM images can visualize key histomorphologic patterns of normal/benign and malignant breast tissues. Small (500 μm × 500 μm) spatially registered SECM and histologic images (n=124 for each) were diagnosed independently by three pathologists with expertise in breast pathology. Diagnostic accuracy of SECM for determining malignant tissues was high, average sensitivity of 0.91, specificity of 0.93, positive predictive value of 0.95, and negative predictive value of 0.87. Intra-observer agreement and inter-observer agreement for SECM were also high, 0.87 and 0.84, respectively. Results from this study suggest that SECM may be developed into an intraoperative margin assessment tool for guiding breast cancer excisions.
Figures

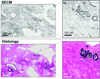

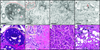

References
-
- Moran MS, Schnitt SJ, Giuliano AE, et al. Society of Surgical Oncology–American Society for Radiation Oncology consensus guideline on margins for breast-conserving surgery with whole-breast irradiation in stages I and II invasive breast cancer. Int J Radiation Oncol Biol Phys. 2014;88:553–564. - PMC - PubMed
-
- McCahill LE, Single RM, Aiello Bowles EJ, et al. Variability in reexcision following breast conservation surgery. JAMA. 2012;307:467–475. - PubMed
-
- Coopey SB, Buckley JM, Smith BL, et al. Lumpectomy cavity shaved margins do not impact re-excision rates in breast cancer patients. Annals of surgical oncology. 2011;18:3036–3040. - PubMed
-
- Boughey JC, Hieken TJ, Jakub JW, et al. Impact of analysis of frozen-section margin on reoperation rates in women undergoing lumpectomy for breast cancer: evaluation of the National Surgical Quality Improvement Program data. Surgery. 2014;156:190–197. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

