A prospective observational study of early intervention with erythropoietin therapy and renal survival in non-dialysis chronic kidney disease patients with anemia: JET-STREAM Study
- PMID: 26779906
- PMCID: PMC5127862
- DOI: 10.1007/s10157-015-1225-9
A prospective observational study of early intervention with erythropoietin therapy and renal survival in non-dialysis chronic kidney disease patients with anemia: JET-STREAM Study
Abstract
Background: There is limited data showing that early treatment for anemia could prolong renal survival in non-dialysis chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients. We therefore investigated the relationship between hemoglobin (Hb) levels at initiation of epoetin beta therapy and renal outcome in non-dialysis CKD patients with anemia.
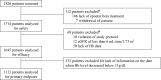
Methods: In this prospective, multi-center, observational study, non-dialysis CKD patients with anemia who were naïve to erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs) were divided into three groups based on their Hb levels at initiation of epoetin beta therapy (Group I: 10 ≤ Hb < 11 g/dL, Group II: 9 ≤ Hb < 10 g/dL, and Group III: Hb < 9 g/dL). The primary endpoint was time to first occurrence of any renal event. For the primary analysis, an inverse probability weighted Cox regression model was used to adjust time-dependent selection bias in the artificially censored data.
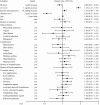
Results: A total of 1113 patients were eligible for primary endpoint analysis. Risk of renal events was significantly higher in Group III compared with Group I (HR, 2.52; 95 % CI, 1.98-3.21; P < 0.0001); although not significant, the risk was also higher in Group II compared with Group I (HR, 1.48; 95 % CI, 0.91-2.40; P = 0.11).
Conclusion: Initiation of ESA therapy when Hb levels decreased below 11 g/dL but not below 10 g/dL could be more effective at reducing the risk of renal events in non-dialysis CKD patients with anemia compared with initiation of ESA therapy at below 9 g/dL or even 10 g/dL.
Keywords: Anemia; Chronic kidney disease; Erythropoiesis-stimulating agents; Non-dialysis; Renal survival.
Conflict of interest statement
Employment/Leadership position/Advisory role: TA (Kyowa Hakko Kirin, Japan Tobacco, Astellas, Nipro), YO (Chugai), MK (Chugai), SK (Chugai). Stock ownership or options: YO (Statocom). Honoraria: TA (Chugai, Bayer, Kyowa Hakko Kirin), YT (Chugai, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Torii), HHi (Chugai, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, Torii, Bayer, FUSO, Astellas), HHa (Chugai, Astellas, Daiichi-Sankyo), SN (Chugai, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, Novartis, Mitsubishi Tanabe), YO (Sanofi). Manuscript fees: TA (Astellas, Kyowa Hakko Kirin), HHi (Chugai, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, Torii, Bayer, FUSO, Astellas). Research funding: YT (Bayer, Asahi Kasei, Otsuka, Eisai), HHa (Chugai, Kyowa Hakko Kirin). Subsidies or Donations: SN (Chugai, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, Astellas, Takeda, Bayer). Endowed departments by commercial entities: YT (Chugai, Baxter). Travel fees, gifts, and others: YO (Yakult, Takeda).
Figures

References
-
- Silverberg D, Wexler D, Blum M, Wollman Y, Iaina A. The cardio-renal anaemia syndrome: does it exist? Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2003;18(suppl 8):viii7–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

