The therapeutic potential of insulin-like growth factor-1 in central nervous system disorders
- PMID: 26780584
- PMCID: PMC4790729
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.01.001
The therapeutic potential of insulin-like growth factor-1 in central nervous system disorders
Abstract
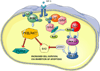
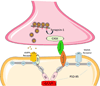
Central nervous system (CNS) development is a finely tuned process that relies on multiple factors and intricate pathways to ensure proper neuronal differentiation, maturation, and connectivity. Disruption of this process can cause significant impairments in CNS functioning and lead to debilitating disorders that impact motor and language skills, behavior, and cognitive functioning. Recent studies focused on understanding the underlying cellular mechanisms of neurodevelopmental disorders have identified a crucial role for insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) in normal CNS development. Work in model systems has demonstrated rescue of pathophysiological and behavioral abnormalities when IGF-1 is administered, and several clinical studies have shown promise of efficacy in disorders of the CNS, including autism spectrum disorder (ASD). In this review, we explore the molecular pathways and downstream effects of IGF-1 and summarize the results of completed and ongoing pre-clinical and clinical trials using IGF-1 as a pharmacologic intervention in various CNS disorders. This aim of this review is to provide evidence for the potential of IGF-1 as a treatment for neurodevelopmental disorders and ASD.
Keywords: ASD; Autism spectrum disorder; CNS development; Central nervous system disorders; Fragile X syndrome; IGF-1; Insulin-like growth factor 1; Neurodevelopmental disorders; Neurotrophic factors; Phelan-McDermid syndrome; Rett syndrome.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Adem A, Ekblom J, Gillberg PG, Jossan SS, Hoog A, Winblad B, Sara V. Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptors in human spinal cord: changes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neural Transm Gen Sect. 1994;97(1):73–84. - PubMed
-
- Aikin R, Maysinger D, Rosenberg L. Cross-talk between phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT and c-jun NH2-terminal kinase mediates survival of isolated human islets. Endocrinology. 2004;145(10):4522–4531. - PubMed
-
- Aleman A, Verhaar HJ, De Haan EH, De Vries WR, Samson MM, Drent ML, Koppeschaar HP. Insulin-like growth factor-I and cognitive function in healthy older men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1999;84(2):471–475. - PubMed
-
- Aman MG, Singh NN, Stewart AW, Field CJ. The aberrant behavior checklist: a behavior rating scale for the assessment of treatment effects. Am J Ment Defic. 1985;89(5):485–491. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association, A. P. A. D. S. M. T. F. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders : DSM-5. 2013 from http://dsm.psychiatryonline.org/book.aspx?bookid=556.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

