The epidemiology of venous thromboembolism
- PMID: 26780736
- PMCID: PMC4715842
- DOI: 10.1007/s11239-015-1311-6
The epidemiology of venous thromboembolism
Abstract
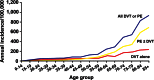
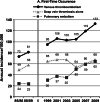
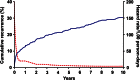
Venous thromboembolism (VTE) is categorized by the U.S. Surgeon General as a major public health problem. VTE is relatively common and associated with reduced survival and substantial health-care costs, and recurs frequently. VTE is a complex (multifactorial) disease, involving interactions between acquired or inherited predispositions to thrombosis and VTE risk factors, including increasing patient age and obesity, hospitalization for surgery or acute illness, nursing-home confinement, active cancer, trauma or fracture, immobility or leg paresis, superficial vein thrombosis, and, in women, pregnancy and puerperium, oral contraception, and hormone therapy. Although independent VTE risk factors and predictors of VTE recurrence have been identified, and effective primary and secondary prophylaxis is available, the occurrence of VTE seems to be relatively constant, or even increasing.
Keywords: Deep vein thrombosis; Epidemiology; Pulmonary embolism; Thrombophlebitis; Venous thromboembolism.
Figures

References
-
- Larsen TB, Sorensen HT, Skytthe A, Johnsen SP, Vaupel JW, Christensen K. Major genetic susceptibility for venous thromboembolism in men: a study of Danish twins. Epidemiology. 2003;14:328–332. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

