Apocynin prevents mitochondrial burdens, microglial activation, and pro-apoptosis induced by a toxic dose of methamphetamine in the striatum of mice via inhibition of p47phox activation by ERK
- PMID: 26780950
- PMCID: PMC4717833
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-016-0478-x
Apocynin prevents mitochondrial burdens, microglial activation, and pro-apoptosis induced by a toxic dose of methamphetamine in the striatum of mice via inhibition of p47phox activation by ERK
Abstract
Background: Activation of NADPH oxidase (PHOX) plays a critical role in mediating dopaminergic neuroinflammation. In the present study, we investigated the role of PHOX in methamphetamine (MA)-induced neurotoxic and inflammatory changes in mice.
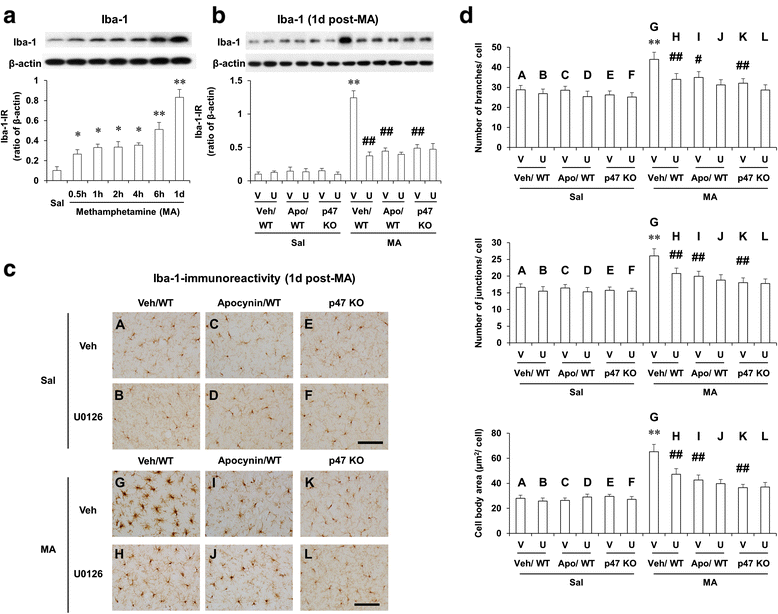
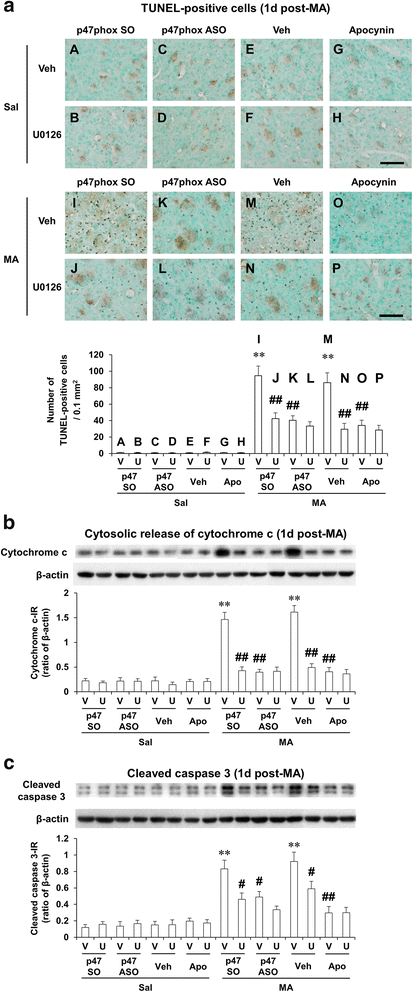
Methods: We examined changes in mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), mitochondrial function [i.e., mitochondrial membrane potential, intramitochondrial Ca(2+) accumulation, mitochondrial oxidative burdens, mitochondrial superoxide dismutase expression, and mitochondrial translocation of the cleaved form of protein kinase C delta type (cleaved PKCδ)], microglial activity, and pro-apoptotic changes [i.e., cytosolic cytochrome c release, cleaved caspase 3, and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUDP nick-end labeling (TUNEL) positive populations] after a neurotoxic dose of MA in the striatum of mice to achieve a better understanding of the effects of apocynin, a non-specific PHOX inhibitor, or genetic inhibition of p47phox (by using p47phox knockout mice or p47phox antisense oligonucleotide) against MA-induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity.
Results: Phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK1/2) was most pronounced out of MAPKs after MA. We observed MA-induced phosphorylation and membrane translocation of p47phox in the striatum of mice. The activation of p47phox promoted mitochondrial stresses followed by microglial activation into the M1 phenotype, and pro-apoptotic changes, and led to dopaminergic impairments. ERK activated these signaling pathways. Apocynin or genetic inhibition of p47phox significantly protected these signaling processes induced by MA. ERK inhibitor U0126 did not exhibit any additional positive effects against protective activity mediated by apocynin or p47phox genetic inhibition, suggesting that ERK regulates p47phox activation, and ERK constitutes the crucial target for apocynin-mediated inhibition of PHOX activation.
Conclusions: Our results indicate that the neuroprotective mechanism of apocynin against MA insult is via preventing mitochondrial burdens, microglial activation, and pro-apoptotic signaling process by the ERK-dependent activation of p47phox.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Ginsenoside Re protects methamphetamine-induced mitochondrial burdens and proapoptosis via genetic inhibition of protein kinase C δ in human neuroblastoma dopaminergic SH-SY5Y cell lines.J Appl Toxicol. 2015 Aug;35(8):927-44. doi: 10.1002/jat.3093. Epub 2014 Dec 18. J Appl Toxicol. 2015. PMID: 25523949
-
PKCδ-dependent p47phox activation mediates methamphetamine-induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity.Free Radic Biol Med. 2018 Feb 1;115:318-337. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.12.018. Epub 2017 Dec 18. Free Radic Biol Med. 2018. PMID: 29269308 Free PMC article.
-
PKCδ knockout mice are protected from para-methoxymethamphetamine-induced mitochondrial stress and associated neurotoxicity in the striatum of mice.Neurochem Int. 2016 Nov;100:146-158. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2016.09.008. Epub 2016 Sep 10. Neurochem Int. 2016. PMID: 27623093 Free PMC article.
-
Role of protein kinase Cδ in dopaminergic neurotoxic events.Food Chem Toxicol. 2018 Nov;121:254-261. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2018.09.005. Epub 2018 Sep 6. Food Chem Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 30195712 Review.
-
Role of Mitochondria in Methamphetamine-Induced Dopaminergic Neurotoxicity: Involvement in Oxidative Stress, Neuroinflammation, and Pro-apoptosis-A Review.Neurochem Res. 2018 Jan;43(1):66-78. doi: 10.1007/s11064-017-2318-5. Epub 2017 Jun 7. Neurochem Res. 2018. PMID: 28589520 Review.
Cited by
-
Neuroinflammation mediates noise-induced synaptic imbalance and tinnitus in rodent models.PLoS Biol. 2019 Jun 18;17(6):e3000307. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000307. eCollection 2019 Jun. PLoS Biol. 2019. PMID: 31211773 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms of programmed cell death in methamphetamine-induced neuronal damage.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 17;13:980340. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.980340. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36059947 Free PMC article.
-
Methamphetamine-induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity as a model of Parkinson's disease.Arch Pharm Res. 2021 Jul;44(7):668-688. doi: 10.1007/s12272-021-01341-7. Epub 2021 Jul 20. Arch Pharm Res. 2021. PMID: 34286473 Review.
-
P2X7 receptor activation aggravates NADPH oxidase 2-induced oxidative stress after intracerebral hemorrhage.Neural Regen Res. 2021 Aug;16(8):1582-1591. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.303036. Neural Regen Res. 2021. PMID: 33433488 Free PMC article.
-
Direct Interaction of Minocycline to p47phox Contributes to its Attenuation of TNF-α-Mediated Neuronal PC12 Cell Death: Experimental and Simulation Validation.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024 Jun;82(2):1261-1277. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01279-9. Epub 2024 May 13. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024. PMID: 38739323
References
-
- Walsh SL, Wagner GC. Motor impairments after methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992;263(2):617–26. - PubMed
-
- Shin EJ, Shin SW, Nguyen TT, Park DH, Wie MB, Jang CG, et al. Ginsenoside Re rescues methamphetamine-induced oxidative damage, mitochondrial dysfunction, microglial activation and dopaminergic degeneration by inhibiting the protein kinase Cδ gene. Mol Neurobiol. 2014;49(3):1400–21. doi: 10.1007/s12035-013-8617-1. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

