Stent dilatation of atretic aortic coarctation in an adult-case report and literature review
- PMID: 26781635
- PMCID: PMC4717556
- DOI: 10.1186/s13019-016-0395-1
Stent dilatation of atretic aortic coarctation in an adult-case report and literature review
Abstract
Background: Patients with functional aortic interruption of the descending thoracic aorta at the isthmus due to severe coarctation in association with atretic lumen are extremely rare in the adult population. The management is challenging and carries high morbidity and mortality.
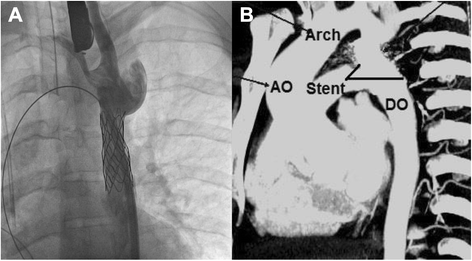
Case presentation: We describe successful percutaneous reconstruction using a covered stent in a similar patient who is doing well two-years after intervention. A literature search was done to explore management strategies and their long-term outcomes for better understanding.
Conclusions: This report is an attempt to highlight the role of minimal invasive approach in the management of rare, severe coarctation of the aorta in adult patients to avoid morbidity and mortality associated with more invasive procedures.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Acquired aortic atresia: Catheter therapy using covered stents.Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2015 Nov 15;86(6):1063-7. doi: 10.1002/ccd.26008. Epub 2015 May 23. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2015. PMID: 26010462
-
Percutaneous treatment of aortic isthmus atresia: use of radiofrequency perforation and covered stents.Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2011 Nov 15;78(6):933-9. doi: 10.1002/ccd.23239. Epub 2011 Aug 8. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2011. PMID: 21805575
-
Coarctation of the aorta in adults: what is the best treatment? Case report and literature review.J Med Life. 2011 May 15;4(2):189-95. Epub 2011 May 25. J Med Life. 2011. PMID: 21776305 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Successful management of a proximally migrated stent in a middle-aged woman with unnoticed native aortic coarctation.Int J Cardiol. 2013 Sep 20;168(1):e19-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2013.05.025. Epub 2013 May 25. Int J Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23711454 No abstract available.
-
Intravascular stenting for the treatment of coarctation of the aorta in adolescent and adult patients.Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2011 Dec;104(12):627-35. doi: 10.1016/j.acvd.2011.08.005. Epub 2011 Nov 21. Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2011. PMID: 22152515 Review.
Cited by
-
Navigating the aftermath: Risk factors of recurrence following coronary bypass surgery in Indonesia.Narra J. 2024 Dec;4(3):e969. doi: 10.52225/narra.v4i3.969. Epub 2024 Oct 11. Narra J. 2024. PMID: 39816076 Free PMC article.
-
Implantation of Covered Stent for Coarctation of the Aorta and Secondary Hypertension in Adolescents-Case Report.Children (Basel). 2021 Nov 5;8(11):1018. doi: 10.3390/children8111018. Children (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34828731 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Musso TM, Slack MC, Nowlen TT. Balloon angioplasty with stenting to correct a functionally interrupted aorta: A case report with three-year follow-up. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2008;72(1):87–92. - PubMed
-
- Sunumlari O. Transcatheter antegrade perforation and covered stent implantation to subatretic coarctation. Anadolu Kardiyol Derg. 2012;12:437–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

