Comprehensive Proteomic Analysis of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Exosomes Reveals Modulation of Angiogenesis via Nuclear Factor-KappaB Signaling
- PMID: 26782178
- PMCID: PMC5785927
- DOI: 10.1002/stem.2298
Comprehensive Proteomic Analysis of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Exosomes Reveals Modulation of Angiogenesis via Nuclear Factor-KappaB Signaling
Abstract
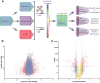
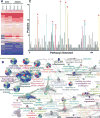
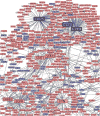
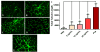
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) are known to facilitate healing of ischemic tissue related diseases through proangiogenic secretory proteins. Recent studies further show that MSC derived exosomes function as paracrine effectors of angiogenesis, however, the identity of which components of the exosome proteome responsible for this effect remains elusive. To address this we used high-resolution isoelectric focusing coupled liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry, an unbiased high throughput proteomics approach to comprehensively characterize the proteinaceous contents of MSCs and MSC derived exosomes. We probed the proteome of MSCs and MSC derived exosomes from cells cultured under expansion conditions and under ischemic tissue simulated conditions to elucidate key angiogenic paracrine effectors present and potentially differentially expressed in these conditions. In total, 6,342 proteins were identified in MSCs and 1,927 proteins in MSC derived exosomes, representing to our knowledge the first time these proteomes have been probed comprehensively. Multilayered analyses identified several putative paracrine effectors of angiogenesis present in MSC exosomes and increased in expression in MSCs exposed to ischemic tissue-simulated conditions; these include platelet derived growth factor, epidermal growth factor, fibroblast growth factor, and most notably nuclear factor-kappaB (NFkB) signaling pathway proteins. NFkB signaling was identified as a key mediator of MSC exosome induced angiogenesis in endothelial cells by functional in vitro validation using a specific inhibitor. Collectively, the results of our proteomic analysis show that MSC derived exosomes contain a robust profile of angiogenic paracrine effectors, which have potential for the treatment of ischemic tissue-related diseases.
Keywords: Exosomes; High-resolution isoelectric focusing; Liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry; Mesenchymal stem cells; Nuclear factor kappaB; Peripheral arterial disease; Proteomics.
© 2016 AlphaMed Press.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors indicate no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Milani RV, Lavie CJ. The role of exercise training in peripheral arterial disease. Vasc Med. 2007;12:351–358. - PubMed
-
- Katz G, Harchandani B, Shah B. Drug-eluting stents: The past, present, and future. Curr Atherosclerosis Rep. 2015;17:485. - PubMed
-
- Yla-Herttuala S, Rissanen TT, Vajanto I, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factors: Biology and current status of clinical applications in cardiovascular medicine. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007;49:1015–1026. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

