Suspected non-Alzheimer disease pathophysiology--concept and controversy
- PMID: 26782335
- PMCID: PMC4784257
- DOI: 10.1038/nrneurol.2015.251
Suspected non-Alzheimer disease pathophysiology--concept and controversy
Abstract
Suspected non-Alzheimer disease pathophysiology (SNAP) is a biomarker-based concept that applies to individuals with normal levels of amyloid-β biomarkers in the brain, but in whom biomarkers of neurodegeneration are abnormal. The term SNAP has been applied to clinically normal individuals (who do not meet criteria for either mild cognitive impairment or dementia) and to individuals with mild cognitive impairment, but is applicable to any amyloid-negative, neurodegeneration-positive individual regardless of clinical status, except when the pathology underlying neurodegeneration can be reliably inferred from the clinical presentation. SNAP is present in ∼23% of clinically normal individuals aged >65 years and in ∼25% of mildly cognitively impaired individuals. APOE*ε4 is underrepresented in individuals with SNAP compared with amyloid-positive individuals. Clinically normal and mildly impaired individuals with SNAP have worse clinical and/or cognitive outcomes than individuals with normal levels of neurodegeneration and amyloid-β biomarkers. In this Perspectives article, we describe the available data on SNAP and address topical controversies in the field.
Conflict of interest statement
C.R.J.Jr has provided consulting services for Eli Lilly and receives research funding from the NIH and the Alexander Family Alzheimer’s Disease Research Professorship of the Mayo Foundation. D.S.K. is a Deputy Editor for
Figures
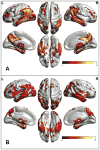
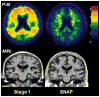
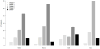
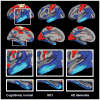
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AG041851/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG034676/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016574/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG003991/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005681/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG026276/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG011378/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS072187/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50‑NS072187/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01‑AG003949/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG003949/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50‑AG016574/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG006786/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

