Decreased SMG7 expression associates with lupus-risk variants and elevated antinuclear antibody production
- PMID: 26783109
- PMCID: PMC4949149
- DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-208441
Decreased SMG7 expression associates with lupus-risk variants and elevated antinuclear antibody production
Abstract
Objectives: Following up the systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) genome-wide association studies (GWAS) identification of NMNAT2 at rs2022013, we fine-mapped its 150 kb flanking regions containing NMNAT2 and SMG7 in a 15 292 case-control multi-ancestry population and tested functions of identified variants.
Methods: We performed genotyping using custom array, imputation by IMPUTE 2.1.2 and allele specific functions using quantitative real-time PCR and luciferase reporter transfections. SLE peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were cultured with small interfering RNAs to measure antinuclear antibody (ANA) and cyto/chemokine levels in supernatants using ELISA.
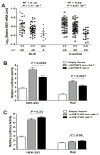
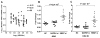
Results: We confirmed association at NMNAT2 in European American (EA) and Amerindian/Hispanic ancestries, and identified independent signal at SMG7 tagged by rs2702178 in EA only (p=2.4×10-8, OR=1.23 (95% CI 1.14 to 1.32)). In complete linkage disequilibrium with rs2702178, rs2275675 in the promoter region robustly associated with SMG7 mRNA levels in multiple expression quantitative trait locus (eQTL) datasets. Its risk allele was dose-dependently associated with decreased SMG7 mRNA levels in PBMCs of 86 patients with SLE and 119 controls (p=1.1×10-3 and 6.8×10-8, respectively) and conferred reduced transcription activity in transfected HEK-293 (human embryonic kidney cell line) and Raji cells (p=0.0035 and 0.0037, respectively). As a critical component in the nonsense-mediated mRNA decay pathway, SMG7 could regulate autoantigens including ribonucleoprotein (RNP) and Smith (Sm). We showed SMG7 mRNA levels in PBMCs correlated inversely with ANA titres of patients with SLE (r=-0.31, p=0.01), and SMG7 knockdown increased levels of ANA IgG and chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 19 in SLE PBMCs (p=2.0×10-5 and 2.0×10-4, respectively).
Conclusion: We confirmed NMNAT2 and identified independent SMG7 association with SLE. The inverse relationship between levels of the risk allele-associated SMG7 mRNAs and ANA suggested the novel contribution of mRNA surveillance pathway to SLE pathogenesis.
Keywords: Autoantibodies; Gene Polymorphism; Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://www.bmj.com/company/products-services/rights-and-licensing/.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Berger F, Lau C, Dahlmann M, et al. Subcellular compartmentation and differential catalytic properties of the three human nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase isoforms. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:36334–41. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1 RR033176/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM104938/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR064820/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AI083790/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000154/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000124/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR033062/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI024717/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U54 TR001018/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002319/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001417/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000004/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AR053308/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI063274/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR020143/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI082714/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 GM103510/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AR065626/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024999/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR053483/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AR062277/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AR064464/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 AR058621/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001422/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR048311/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR043814/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI028697/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI024717/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR042460/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR057172/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI101934/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025014/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR029882/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- L30 AI071651/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR043727/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA141700/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001082/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AI078004/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AR002138/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R21 AI070304/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI083194/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AR049084/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR051545/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR043274/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AR062755/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

