Vascular complications following liver transplantation: A literature review of advances in 2015
- PMID: 26783420
- PMCID: PMC4705452
- DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i1.36
Vascular complications following liver transplantation: A literature review of advances in 2015
Abstract
Although vascular complications (VCs) following orthotopic liver transplantation (OLT) seldom occur, they are the most feared complications with a high incidence of both graft loss and mortality, as they compromise the blood flow of the transplant (either inflow or outflow). Diagnosis and therapeutic management of VCs constitute a major challenge in terms of increasing the success rate of liver transplantation. While surgical treatment used to be considered the first choice for management, advances in endovascular intervention have increased to make this a viable therapeutic option. Considering VC as a rare but a major and dreadful issue in OLT history, and in view of the continuing and rapid progress in recent years, an update on these uncommon conditions seemed necessary. In this sense, this review comprehensively discusses the important features (epidemiological, clinical, paraclinical, prognostic and therapeutic) of VCs following OLT.
Keywords: Endovascular intervention; Liver transplantation; Orthotopic liver transplantation; Vascular complications.
Figures
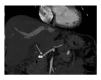

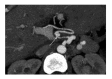


References
-
- Khalaf H. Vascular complications after deceased and living donor liver transplantation: a single-center experience. Transplant Proc. 2010;42:865–870. - PubMed
-
- Karatzas T, Lykaki-Karatzas E, Webb M, Nery J, Tsaroucha A, Demirbas A, Khan F, Ciancio G, Montalvo B, Reddy R, et al. Vascular complications, treatment, and outcome following orthotopic liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 1997;29:2853–2855. - PubMed
-
- Pawlak J, Grodzicki M, Leowska E, Małkowski P, Michałowicz B, Nyckowski P, Rowiński O, Pacho R, Zieniewicz K, Andrzejewska M, et al. Vascular complications after liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2003;35:2313–2315. - PubMed
-
- Duffy JP, Hong JC, Farmer DG, Ghobrial RM, Yersiz H, Hiatt JR, Busuttil RW. Vascular complications of orthotopic liver transplantation: experience in more than 4,200 patients. J Am Coll Surg. 2009;208:896–903; discussion 903-905. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

