De novo mutations in congenital heart disease with neurodevelopmental and other congenital anomalies
- PMID: 26785492
- PMCID: PMC4890146
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aac9396
De novo mutations in congenital heart disease with neurodevelopmental and other congenital anomalies
Abstract
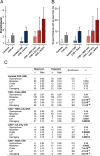
Congenital heart disease (CHD) patients have an increased prevalence of extracardiac congenital anomalies (CAs) and risk of neurodevelopmental disabilities (NDDs). Exome sequencing of 1213 CHD parent-offspring trios identified an excess of protein-damaging de novo mutations, especially in genes highly expressed in the developing heart and brain. These mutations accounted for 20% of patients with CHD, NDD, and CA but only 2% of patients with isolated CHD. Mutations altered genes involved in morphogenesis, chromatin modification, and transcriptional regulation, including multiple mutations in RBFOX2, a regulator of mRNA splicing. Genes mutated in other cohorts examined for NDD were enriched in CHD cases, particularly those with coexisting NDD. These findings reveal shared genetic contributions to CHD, NDD, and CA and provide opportunities for improved prognostic assessment and early therapeutic intervention in CHD patients.
Copyright © 2015, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures


References
-
- Marino BS, et al. Neurodevelopmental outcomes in children with congenital heart disease: evaluation and management: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2012;126:1143–1172. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UM1 HL098162/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 HL098123/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- U01 HL098162/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007208/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 HL098166/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UP_1102/20/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- T32 GM007205/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- ARC_/Arthritis Research UK/United Kingdom
- MR/K006584/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- UM1 HL098147/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

