Peanuts as functional food: a review
- PMID: 26787930
- PMCID: PMC4711439
- DOI: 10.1007/s13197-015-2007-9
Peanuts as functional food: a review
Erratum in
-
Correction: Peanuts as functional food: a review.J Food Sci Technol. 2024 Nov;61(11):2222. doi: 10.1007/s13197-024-06021-0. Epub 2024 Jun 29. J Food Sci Technol. 2024. PMID: 39397841 Free PMC article.
Abstract
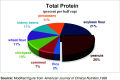
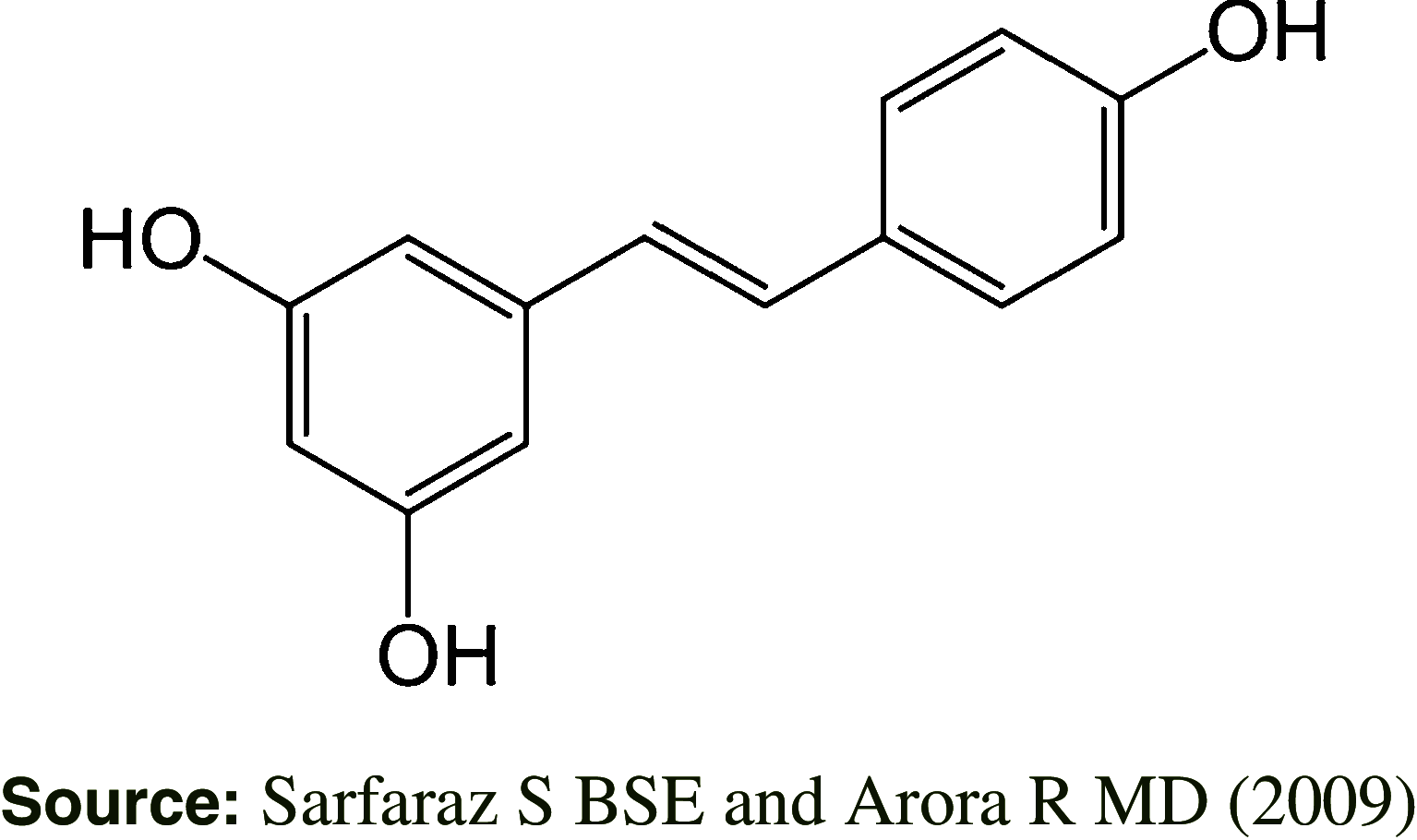
Peanut is an important crop grown worldwide. Commercially it is used mainly for oil production but apart from oil, the by-products of peanut contains many other functional compounds like proteins, fibers, polyphenols, antioxidants, vitamins and minerals which can be added as a functional ingredient into many processed foods. Recently it has also revealed that peanuts are excellent source of compounds like resveratrol, phenolic acids, flavonoids and phytosterols that block the absorption of cholesterol from diet. It is also a good source of Co-enzyme Q10 and contains all the 20 amino acids with highest amount of arginine. These bioactive compounds have been recognized for having disease preventive properties and are thought to promote longevity. The processing methods like roasting and boiling have shown increase in the concentration of these bioactive compounds. In the present paper an overview on peanut bioactive constituents and their health benefits are presented.
Keywords: Functional ingredients; Health benefits; Peanut.
Figures

References
-
- Abbas M, Asi MR, Anwar F, Mahmood T, Khan AM, Yaqub T (2013) Assessment of aflatoxins in peanuts grown in the Pothohar area of Pakistan . Food Additives and Contaminants Part B 1–5. doi:10.1080/19393210.2013.820221 - PubMed
-
- Alper CM, Mattes RD (2002) Effects of chronic peanut consumption on energy balance and hedonics. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord: J Int Assoc Stud Obes 26(8):1129–1137 - PubMed
-
- Awad AB, Chan KC, Downie AC, Fink CS (2000) Peanuts as a source of β-sitosterol, a sterol with anticancer properties. Nutr Cancer 36(2):238–241 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
